Finasteride does not increase the risk of high-grade prostate cancer: a bias-adjusted modeling approach
- PMID: 19138953
- PMCID: PMC2844801
- DOI: 10.1158/1940-6207.CAPR-08-0092
Finasteride does not increase the risk of high-grade prostate cancer: a bias-adjusted modeling approach
Abstract
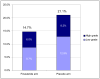
Finasteride taken for 7 years in the Prostate Cancer Prevention Trial (PCPT) reduced the risk of prostate cancer by 25%, but with an apparent increased risk of high-grade disease. Subsequent analyses found that finasteride biases toward improved prostate cancer detection and accuracy in prostate cancer grading at biopsy. In our first analysis of the present study, we accounted for these biases in estimating the effect of finasteride on the risk of overall and high-grade prostate cancer. This analysis used PCPT data that included 3-month longer collection of endpoints than in the original report with observed prostate cancer rates of 22.9% (4.8% with high grade; placebo) versus 16.6% (5.8% with high grade; finasteride). Based on these updated results, the bias-adjusted prostate cancer rates are estimated to be 21.1% (4.2% high grade; placebo) and 14.7% (4.8% high grade; finasteride), a 30% risk reduction in prostate cancer [relative risk (RR), 0.70; 95% confidence interval (95% CI), 0.64-0.76; P < 0.0001] and a nonsignificant 14% increase in high-grade cancer (RR, 1.14; 95% CI, 0.96-1.35; P = 0.12) with finasteride. We then estimated rates of high-grade prostate cancer based on an analysis that incorporated grading information from radical prostatectomies in 500 subjects diagnosed with cancer. The resulting estimates were high-grade cancer rates of 8.2% (placebo) versus 6.0% (finasteride), a 27% risk reduction (RR, 0.73; 95% CI, 0.56-0.96; P = 0.02) with finasteride. Our third analysis examined the impact of biopsy sensitivity on the relative risk of high-grade prostate cancer and found that differential sensitivity of biopsy between the treatment arms can have a significant impact on risk ratio estimates. These collective results suggest that the observed, unadjusted higher risk of high-grade disease with finasteride seems to have been due to facilitated diagnosis resulting primarily from increased biopsy sensitivity with finasteride. Therefore, men undergoing regular prostate cancer screening or who express an interest in cancer prevention should be informed of the opportunity to take finasteride for preventing prostate cancer.
Figures
Comment in
-
High-grade prostate cancer and the prostate cancer prevention trial.Cancer Prev Res (Phila). 2008 Aug;1(3):151-2. doi: 10.1158/1940-6207.CAPR-08-0085. Epub 2008 May 18. Cancer Prev Res (Phila). 2008. PMID: 19138948 No abstract available.
-
Finasteride and high-grade prostate cancer.Cancer Prev Res (Phila). 2009 Feb;2(2):185; author reply 185. doi: 10.1158/1940-6207.CAPR-08-0117. Epub 2009 Jan 27. Cancer Prev Res (Phila). 2009. PMID: 19174583 No abstract available.
-
Words of wisdom. Re: Pathologic characteristics of cancers detected in the Prostate Cancer Prevention Trial: implications for prostate cancer detection and chemoprevention.Eur Urol. 2009 Feb;55(2):522-3. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2008.11.015. Eur Urol. 2009. PMID: 19606534 No abstract available.
References
-
- Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, Murray T, Xu J, Thun MJ. Cancer Statistics, 2007. CA Cancer J Clin. 2007;57:43–66. - PubMed
-
- Gohagan JK, Prorok PC, Hayes RB, et al. The Prostate, Lung, Colorectal and Ovarian (PLCO) Cancer Screening Trial of the National Cancer Institute: history, organization, and status. Control Clin Trials. 2000;21:251–72S. - PubMed
-
- de Koning HJ, Auvinen A, Berenguer Sanchez A, et al. Large-scale randomized prostate cancer screening trials: program performances in the European Randomized Screening for Prostate Cancer trial and the Prostate, Lung, Colorectal and Ovary Cancer trial. Int J Cancer. 2002;97:237–44. - PubMed
-
- Thompson IM, Goodman PJ, Tangen CM, Lucia MS, Miller GJ, Ford LG, Lieber MM, Cespedes RD, Atkins JN, Lippman SM, Carlin SM, Ryan A, Szczepanek CM, Crowley JJ, Coltman CA., Jr. The influence of finasteride on the development of prostate cancer. N Engl J Med. 2003;349:215–24. - PubMed
-
- Scardino PT. The prevention of prostate cancer - the dilemma continues. New England Journal of Medicine. 2003;349:297–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

