Helicobacter pylori and esophageal cancer risk: a meta-analysis
- PMID: 19138977
- PMCID: PMC3501739
- DOI: 10.1158/1940-6207.CAPR-08-0109
Helicobacter pylori and esophageal cancer risk: a meta-analysis
Abstract
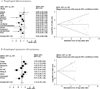
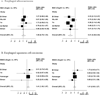
We conducted this meta-analysis to examine the association between Helicobacter pylori and esophageal adenocarcinoma (EAC) and esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. We searched the PubMed database, the ISI database, and the references of the selected articles. Case-control or nested case-control studies were selected if they used serology or endoscopic methods to detect H. pylori in the stomach and if control subjects were not restricted to upper gastrointestinal tract cancer or peptic ulcer disease patients. A total of 19 studies were used for this analysis. Summary odds ratios (OR) and 95% confidence intervals (95% CI) were calculated using the DerSimonian-Laird method. Q statistics and I(2) statistics were calculated to examine heterogeneity. Subgroup analyses were conducted by CagA status. For EAC, the summary OR (95% CI) was 0.56 (0.46-0.68). There was little heterogeneity among studies (I(2) = 15%). Further analysis showed that colonization with CagA-positive strains was inversely associated with EAC risk (OR, 0.41; 95% CI, 0.28-0.62) but colonization with CagA-negative strains was not (OR, 1.08; 95% CI, 0.76-1.53). For esophageal squamous cell carcinoma, the summary OR (95% CI) was 1.10 (0.78-1.55). However, there was substantial heterogeneity among studies (I(2) = 73%), with statistically significant associations in both directions. Our results suggest an inverse association between CagA-positive H. pylori colonization and risk of EAC. The prominent decline of H. pylori colonization in the past few decades may be partly responsible for the recent increase in EAC incidence in Western countries.
Conflict of interest statement
None
Figures
Comment in
-
Disappearing microbiota: Helicobacter pylori protection against esophageal adenocarcinoma.Cancer Prev Res (Phila). 2008 Oct;1(5):308-11. doi: 10.1158/1940-6207.CAPR-08-0170. Cancer Prev Res (Phila). 2008. PMID: 19138974 No abstract available.
-
The role of Helicobacter pylori in the spectrum of Barrett's carcinogenesis.Cancer Prev Res (Phila). 2009 Jan;2(1):94. doi: 10.1158/1940-6207.CAPR-08-0194. Cancer Prev Res (Phila). 2009. PMID: 19139023 No abstract available.
References
-
- Marshall BJ, Warren JR. Unidentified curved bacilli in the stomach of patients with gastritis and peptic ulceration. Lancet. 1984;1:1311–1315. - PubMed
-
- Suerbaum S, Michetti P. Helicobacter pylori infection. N Engl J Med. 2002;347:1175–1186. - PubMed
-
- Raderer M, Wrba F, Kornek G, et al. Association between Helicobacter pylori infection and pancreatic cancer. Oncology. 1998;55:16–19. - PubMed
-
- Stolzenberg-Solomon RZ, Blaser MJ, Limburg PJ, et al. Helicobacter pylori seropositivity as a risk factor for pancreatic cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2001;93:937–941. - PubMed
-
- Limburg PJ, Stolzenberg-Solomon RZ, Colbert LH, et al. Helicobacter pylori seropositivity and colorectal cancer risk: a prospective study of male smokers. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2002;11:1095–1099. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous