Genome-wide analysis to predict protein sequence variations that change phosphorylation sites or their corresponding kinases
- PMID: 19139070
- PMCID: PMC2651802
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkn1008
Genome-wide analysis to predict protein sequence variations that change phosphorylation sites or their corresponding kinases
Abstract
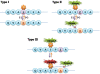
We define phosphovariants as genetic variations that change phosphorylation sites or their interacting kinases. Considering the essential role of phosphorylation in protein functions, it is highly likely that phosphovariants change protein functions. Therefore, a comparison of phosphovariants between individuals or between species can give clues about phenotypic differences. We categorized phosphovariants into three subtypes and developed a system that predicts them. Our method can be used to screen important polymorphisms and help to identify the mechanisms of genetic diseases.
Figures

References
-
- Hunter T. Signaling–2000 and beyond. Cell. 2000;100:113–127. - PubMed
-
- Dash PK, Moore AN, Kobori N, Runyan JD. Molecular activity underlying working memory. Learn. Mem. 2007;14:554–563. - PubMed
-
- Hunter T, Karin M. The regulation of transcription by phosphorylation. Cell. 1992;70:375–387. - PubMed
-
- Beausoleil SA, Villen J, Gerber SA, Rush J, Gygi SP. A probability-based approach for high-throughput protein phosphorylation analysis and site localization. Nat. Biotechnol. 2006;24:1285–1292. - PubMed
-
- Olsen JV, Blagoev B, Gnad F, Macek B, Kumar C, Mortensen P, Mann M. Global, in vivo, and site-specific phosphorylation dynamics in signaling networks. Cell. 2006;127:635–648. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

