Structure, binding, and activity of Syd, a SecY-interacting protein
- PMID: 19139097
- PMCID: PMC2658082
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M808305200
Structure, binding, and activity of Syd, a SecY-interacting protein
Abstract
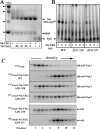
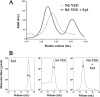
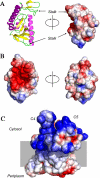
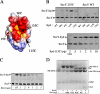
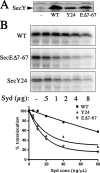
The Syd protein has been implicated in the Sec-dependent transport of polypeptides across the bacterial inner membrane. Using Nanodiscs, we here provide direct evidence that Syd binds the SecY complex, and we demonstrate that interaction involves the two electropositive and cytosolic loops of the SecY subunit. We solve the crystal structure of Syd and together with cysteine cross-link analysis, we show that a conserved concave and electronegative groove constitutes the SecY-binding site. At the membrane, Syd decreases the activity of the translocon containing loosely associated SecY-SecE subunits, whereas in detergent solution Syd disrupts the SecYEG heterotrimeric associations. These results support the role of Syd in proofreading the SecY complex biogenesis and point to the electrostatic nature of the Sec channel interaction with its cytosolic partners.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Three-dimensional structure of the bacterial protein-translocation complex SecYEG.Nature. 2002 Aug 8;418(6898):662-5. doi: 10.1038/nature00827. Nature. 2002. PMID: 12167867
-
Genetic analysis of an essential cytoplasmic domain of Escherichia coli SecY based on resistance to Syd, a SecY-interacting protein.Mol Gen Genet. 1998 May;258(3):240-9. doi: 10.1007/s004380050728. Mol Gen Genet. 1998. PMID: 9645430
-
Mapping the sites of interaction between SecY and SecE by cysteine scanning mutagenesis.J Biol Chem. 2001 Aug 31;276(35):32559-66. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M103912200. Epub 2001 Jul 9. J Biol Chem. 2001. PMID: 11445571
-
The SecY translocation complex: convergence of genetics and structure.Trends Microbiol. 2007 May;15(5):203-10. doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2007.03.001. Epub 2007 Mar 23. Trends Microbiol. 2007. PMID: 17368028 Review.
-
Translocation of proteins through the Sec61 and SecYEG channels.Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2009 Aug;21(4):501-7. doi: 10.1016/j.ceb.2009.04.010. Epub 2009 May 18. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2009. PMID: 19450960 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Investigating the stability of the SecA-SecYEG complex during protein translocation across the bacterial membrane.J Biol Chem. 2019 Mar 8;294(10):3577-3587. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA118.006447. Epub 2019 Jan 2. J Biol Chem. 2019. PMID: 30602566 Free PMC article.
-
Uncovering the Optimal Molecular Characteristics of Hydrophobe-Containing Polypeptoids to Induce Liposome or Cell Membrane Fragmentation.Biomacromolecules. 2023 Mar 13;24(3):1511-1521. doi: 10.1021/acs.biomac.3c00028. Epub 2023 Feb 21. Biomacromolecules. 2023. PMID: 36802533 Free PMC article.
-
Nanodisc-based co-immunoprecipitation for mass spectrometric identification of membrane-interacting proteins.Mol Cell Proteomics. 2011 Jul;10(7):O110.006775. doi: 10.1074/mcp.O110.006775. Epub 2011 Apr 30. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2011. PMID: 21532009 Free PMC article.
-
Physicochemical factors controlling the activity and energy coupling of an ionic strength-gated ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporter.J Biol Chem. 2013 Oct 11;288(41):29862-71. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.499327. Epub 2013 Aug 26. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23979139 Free PMC article.
-
Nanodiscs: A Controlled Bilayer Surface for the Study of Membrane Proteins.Annu Rev Biophys. 2018 May 20;47:107-124. doi: 10.1146/annurev-biophys-070816-033620. Epub 2018 Mar 1. Annu Rev Biophys. 2018. PMID: 29494254 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rapoport, T. A. (2007) Nature 450 663-669 - PubMed
-
- Menetret, J. F., Schaletzky, J., Clemons, W. M., Jr., Osborne, A. R., Skanland, S. S., Denison, C., Gygi, S. P., Kirkpatrick, D. S., Park, E., Ludtke, S. J., Rapoport, T. A., and Akey, C. W. (2007) Mol. Cell 28 1083-1092 - PubMed
-
- Schiebel, E., Driessen, A. J., Hartl, F. U., and Wickner, W. (1991) Cell 64 927-939 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

