Natural micropolymorphism in human leukocyte antigens provides a basis for genetic control of antigen recognition
- PMID: 19139173
- PMCID: PMC2626662
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20082136
Natural micropolymorphism in human leukocyte antigens provides a basis for genetic control of antigen recognition
Abstract
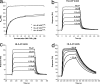
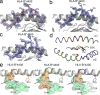
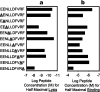
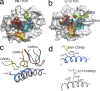
Human leukocyte antigen (HLA) gene polymorphism plays a critical role in protective immunity, disease susceptibility, autoimmunity, and drug hypersensitivity, yet the basis of how HLA polymorphism influences T cell receptor (TCR) recognition is unclear. We examined how a natural micropolymorphism in HLA-B44, an important and large HLA allelic family, affected antigen recognition. T cell-mediated immunity to an Epstein-Barr virus determinant (EENLLDFVRF) is enhanced when HLA-B*4405 was the presenting allotype compared with HLA-B*4402 or HLA-B*4403, each of which differ by just one amino acid. The micropolymorphism in these HLA-B44 allotypes altered the mode of binding and dynamics of the bound viral epitope. The structure of the TCR-HLA-B*4405(EENLLDFVRF) complex revealed that peptide flexibility was a critical parameter in enabling preferential engagement with HLA-B*4405 in comparison to HLA-B*4402/03. Accordingly, major histocompatibility complex (MHC) polymorphism can alter the dynamics of the peptide-MHC landscape, resulting in fine-tuning of T cell responses between closely related allotypes.
Figures

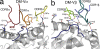
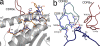
References
-
- Messaoudi, I., J.A. Patino, R. Dyall, J. LeMaoult, and J. Nikolich-Zugich. 2002. Direct link between MHC polymorphism, T cell avidity, and diversity in immune defense. Science. 298:1797–1800. - PubMed
-
- DiBrino, M., K.C. Parker, D.H. Margulies, J. Shiloach, R.V. Turner, W.E. Biddison, and J.E. Coligan. 1995. Identification of the peptide binding motif for HLA-B44, one of the most common HLA-B alleles in the Caucasian population. Biochemistry. 34:10130–10138. - PubMed
-
- Godfrey, D.I., J. Rossjohn, and J. McCluskey. 2008. The fidelity, occasional promiscuity, and versatility of T cell receptor recognition. Immunity. 28:304–314. - PubMed
-
- Clements, C.S., M.A. Dunstone, W.A. Macdonald, J. McCluskey, and J. Rossjohn. 2006. Specificity on a knife-edge: the alphabeta T cell receptor. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 16:787–795. - PubMed
-
- Rudolph, M.G., R.L. Stanfield, and I.A. Wilson. 2006. How TCRs bind MHCs, peptides, and coreceptors. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 24:419–466. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

