SALL3 interacts with DNMT3A and shows the ability to inhibit CpG island methylation in hepatocellular carcinoma
- PMID: 19139273
- PMCID: PMC2655625
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.00840-08
SALL3 interacts with DNMT3A and shows the ability to inhibit CpG island methylation in hepatocellular carcinoma
Abstract
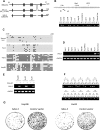
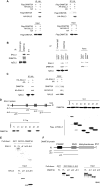
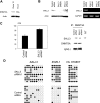
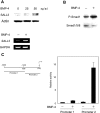
The mechanisms of aberrant CpG island methylation in oncogenesis are not fully characterized. In particular, little is known about the mechanisms of inhibition of CpG island methylation. Here we show that sal-like 3 (SALL3) is a novel inhibitory factor for DNA methyltransferase 3 alpha (DNMT3A). SALL3 binds to DNMT3A by a direct interaction between the double zinc finger motif of SALL3 and the PWWP domain of DNMT3A. SALL3 expression reduces DNMT3A-mediated CpG island methylation in cell culture and in vitro. CpG island methylation is enhanced in SALL3-depleted cells. Consistently, DNMT3A from SALL3-depleted cells increases methyltransferase activity in vitro. Binding of DNMT3A to chromatin is reduced or increased by SALL3 expression or depletion, respectively, accounting for the mechanism by which SALL3 inhibits DNMT3A-mediated CpG island methylation. We also show that SALL3 is inducible by BMP-4 and silenced by associated DNA methylation in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Our results suggest that silencing of SALL3 results in acceleration of DNA methylation in HCC. This functional characterization of SALL3 sheds light on regulatory mechanisms for DNMT3A and provides new strategies to inhibit aberrant methylation in cancer.
Figures



References
-
- Bachman, K. E., B. H. Park, I. Rhee, H. Rajagopalan, J. G. Herman, S. B. Baylin, K. W. Kinzler, and B. Vogelstein. 2003. Histone modifications and silencing prior to DNA methylation of a tumor suppressor gene. Cancer Cell 389-95. - PubMed
-
- Bird, A. 1992. The essentials of DNA methylation. Cell 705-8. - PubMed
-
- Bohm, J., F. J. Kaiser, W. Borozdin, R. Depping, and J. Kohlhase. 2007. Synergistic cooperation of Sall4 and Cyclin D1 in transcriptional repression. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 356773-779. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
