Therapeutic efficacy of ipilimumab, an anti-CTLA-4 monoclonal antibody, in patients with metastatic melanoma unresponsive to prior systemic treatments: clinical and immunological evidence from three patient cases
- PMID: 19139884
- PMCID: PMC11030873
- DOI: 10.1007/s00262-008-0642-y
Therapeutic efficacy of ipilimumab, an anti-CTLA-4 monoclonal antibody, in patients with metastatic melanoma unresponsive to prior systemic treatments: clinical and immunological evidence from three patient cases
Abstract
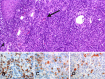
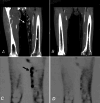
The management of unresectable metastatic melanoma is a major clinical challenge because of the lack of reliably effective systemic therapies. Blocking cytotoxic T lymphocyte-associated antigen-4 (CTLA-4) has recently been proposed as a strategy to enhance cell-mediated immune responses to cancer, and clinical trials have demonstrated that anti-CTLA-4 therapy can produce durable outcomes with different response patterns than cytotoxic chemotherapy. We enrolled eight out of 155 patients with advanced melanoma in a multicentre phase II trial that evaluated the activity and tolerability of ipilimumab, a fully human, anti-CTLA-4 monoclonal antibody ( www.clinicaltrials.gov ; NCT00289627; CA184-008). Here we report our experience with three of these patients, who experienced progressive disease after a variety of previous therapies, including prior immunotherapies, and who achieved good outcomes with ipilimumab. One patient had a partial response ongoing at 17+ months on ipilimumab despite failure with four prior therapies, and the other two patients showed durable stable disease, both still ongoing at 17+ and 20+ months, respectively. The patient achieving a partial response experienced no side effects while receiving ipilimumab. The other two patients developed immune-related adverse events (irAEs) including rash (one case; grade 2) and diarrhoea (both cases; grades 1 and 2, respectively); the histopathology of colon biopsy samples from both was suggestive of colitis, with an abundant CD8+ T-cell infiltrate. Nausea, vomiting and acute pancreatitis were also observed in one patient. In addition, immunohistochemical findings of a dense CD8+, TIA1+ and granzyme B+ lymphoid infiltrate within a biopsied lesion provide indirect evidence of functional T-cell activation induced by treatment. These case reports highlight the potential for anti-CTLA-4-based therapy in previously treated patients with advanced melanoma. Moreover, because the patterns of response to ipilimumab differ from chemotherapy, we need to understand how and when patients may respond to treatment so that appropriate clinical decisions can be made.
Figures



References
-
- Atkins MB, Lotze MT, Dutcher JP, Fisher RI, Weiss G, Margolin K, Abrams J, Sznol M, Parkinson D, Hawkins M, Paradise C, Kunkel L, Rosenberg SA. High-dose recombinant interleukin 2 therapy for patients with metastatic melanoma: analysis of 270 patients treated between 1985 and 1993. J Clin Oncol. 1999;17:2105–2116. - PubMed
-
- Attia P, Phan GQ, Maker AV, Robinson MR, Quezado MM, Yang JC, Sherry RM, Topalian SL, Kammula US, Royal RE, Restifo NP, Haworth LR, Levy C, Mauroukakis SA, Nichol G, Yellin MJ, Rosenberg SA. Autoimmunity correlates with tumor regression in patients with metastatic melanoma treated with anti-cytotoxic T-lymphocyte antigen-4. J Clin Oncol. 2005;23:6043–6053. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2005.06.205. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Beck KE, Blansfield JA, Tran KQ, Feldan AL, Hughes MS, Royal RE, Kammula US, Topalian SL, Sherry RM, Kleiner D, Quezado M, Lowy I, Yellin M, Rosenberg SA, Yang JC. Enterocolitis in patients with cancer after antibody blockade of cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated antigen 4. J Clin Oncol. 2006;24:2283–2289. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2005.04.5716. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chen B, Phillips J, Greenbaum M, Klitzing D, Cardarelli PM, Korman A (2007) Efficacy of anti-CTLA-4 antibody in the Sa1 N tumor model when combined with dexamethasone (abstract 2202). In: Presented at the AACR Annual Meeting, 14–28 April 2007, Los Angeles, CA, USA
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

