A structural explanation for the binding of endocytic dileucine motifs by the AP2 complex
- PMID: 19140243
- PMCID: PMC4340503
- DOI: 10.1038/nature07422
A structural explanation for the binding of endocytic dileucine motifs by the AP2 complex
Abstract
Most transmembrane proteins are selected as transport vesicle cargo through the recognition of short, linear amino acid motifs in their cytoplasmic portions by vesicle coat proteins. In the case of clathrin-coated vesicles (CCVs) the motifs are recognised by clathrin adaptors. The AP2 adaptor complex (subunits α,β2,μ2,σ2) recognises both major endocytic motifs: YxxΦ motifs and [DE]xxxL[LI] acidic dileucine motifs. Here we describe the binding of AP2 to the endocytic dileucine motif from CD4 . The major recognition events are the two leucine residues binding in hydrophobic pockets on σ2. The hydrophilic residue four residues upstream from the first leucine sits on a positively charged patch made from residues on σ2 and α subunits. Mutations in key residues inhibit the binding of AP2 to ‘acidic dileucine’ motifs displayed in liposomes containing PtdIns4,5P2, but do not affect binding to YxxΦ motifs via μ2. In the ‘inactive’ AP2 core structure , both motif binding sites are blocked by different parts of the β2 subunit. To allow a dileucine motif to bind, the β2 N-terminus is displaced and becomes disordered; however, in this structure the YxxΦ binding site on μ2 remains blocked.
Figures
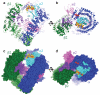

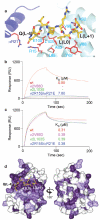
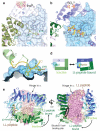
References
-
- Collins BM, McCoy AJ, Kent HM, Evans PR, Owen DJ. Molecular architecture and functional model of the endocytic AP2 complex. Cell. 2002;109:523–35. - PubMed
Additional References for online Materials and Methods
-
- Leslie AG. The integration of macromolecular diffraction data. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 2006;62:48–57. - PubMed
-
- Evans P. Scaling and assessment of data quality. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 2006;62:72–82. - PubMed
-
- Adams PD, et al. PHENIX: building new software for automated crystallographic structure determination. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 2002;58:1948–54. - PubMed
-
- Emsley P, Cowtan K. Coot: Model-Building Tools for Molecular Graphics. Acta Crystallographica Section D - Biological Crystallography. 2004;60:2126–2132. - PubMed
-
- Painter J, Merritt EA. Optimal description of a protein structure in terms of multiple groups undergoing TLS motion. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 2006;62:439–50. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

