Knockdown of m-calpain increases survival of primary hippocampal neurons following NMDA excitotoxicity
- PMID: 19141074
- PMCID: PMC2676331
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2008.05860.x
Knockdown of m-calpain increases survival of primary hippocampal neurons following NMDA excitotoxicity
Abstract
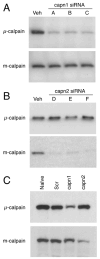
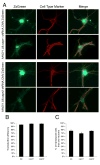
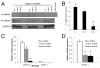
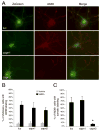
The calpain family of cysteine proteases has a well-established causal role in neuronal cell death following acute brain injury. However, the relative contribution of calpain isoforms to the various forms of injury has not been determined as available calpain inhibitors are not isoform-specific. In this study, we evaluated the relative role of m-calpain and mu-calpain in a primary hippocampal neuron model of NMDA-mediated excitotoxicity. Baseline mRNA expression for the catalytic subunit of m-calpain (capn2 ) was found to be 50-fold higher than for the mu-calpain catalytic subunit (capn1) based on quantitative real-time PCR. Adeno-associated viral vectors designed to deliver short hairpin RNAs targeting capn1 or capn2 resulted in 60% and 90% knockdown of message respectively. Knockdown of capn2 but not capn1 increased neuronal survival after NMDA exposure at 21 days in vitro. Nuclear translocation of calpain substrates apoptosis inducing factor, p35/p25 and collapsin response mediator protein (CRMP) 2-4 was not detected after NMDA exposure in this model. However, nuclear translocation of CRMP-1 was observed and was prevented by capn2 knockdown. These findings provide insight into potential mechanisms of calpain-mediated neurodegeneration and have important implications for the development of isoform-specific calpain inhibitor therapy.
Figures


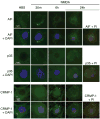
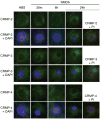
References
-
- Ai J, Liu E, Wang J, Chen Y, Yu J, Baker AJ. Calpain inhibitor MDL-28170 reduces the functional and structural deterioration of corpus callosum following fluid percussion injury. J Neurotrauma. 2007;24:960–978. - PubMed
-
- Bano D, Young KW, Guerin CJ, Lefeuvre R, Rothwell NJ, Naldini L, Rizzuto R, Carafoli E, Nicotera P. Cleavage of the plasma membrane Na+/Ca2+ exchanger in excitotoxicity. Cell. 2005;120:275–285. - PubMed
-
- Bartus RT, Baker KL, Heiser AD, Sawyer SD, Dean RL, Elliott PJ, Straub JA. Postischemic administration of AK275, a calpain inhibitor, provides substantial protection against focal ischemic brain damage. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1994a;14:537–544. - PubMed
-
- Bartus RT, Dean RL, Cavanaugh K, Eveleth D, Carriero DL, Lynch G. Time-related neuronal changes following middle cerebral artery occlusion: implications for therapeutic intervention and the role of calpain. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1995;15:969–979. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

