STARCH-EXCESS4 is a laforin-like Phosphoglucan phosphatase required for starch degradation in Arabidopsis thaliana
- PMID: 19141707
- PMCID: PMC2648081
- DOI: 10.1105/tpc.108.064360
STARCH-EXCESS4 is a laforin-like Phosphoglucan phosphatase required for starch degradation in Arabidopsis thaliana
Abstract
Starch is the major storage carbohydrate in plants. It is comprised of glucans that form semicrystalline granules. Glucan phosphorylation is a prerequisite for normal starch breakdown, but phosphoglucan metabolism is not understood. A putative protein phosphatase encoded at the Starch Excess 4 (SEX4) locus of Arabidopsis thaliana was recently shown to be required for normal starch breakdown. Here, we show that SEX4 is a phosphoglucan phosphatase in vivo and define its role within the starch degradation pathway. SEX4 dephosphorylates both the starch granule surface and soluble phosphoglucans in vitro, and sex4 null mutants accumulate phosphorylated intermediates of starch breakdown. These compounds are linear alpha-1,4-glucans esterified with one or two phosphate groups. They are released from starch granules by the glucan hydrolases alpha-amylase and isoamylase. In vitro experiments show that the rate of starch granule degradation is increased upon simultaneous phosphorylation and dephosphorylation of starch. We propose that glucan phosphorylating enzymes and phosphoglucan phosphatases work in synergy with glucan hydrolases to mediate efficient starch catabolism.
Figures



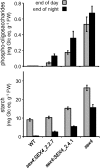




References
-
- Alonso, A., Sasin, J., Bottini, N., Friedberg, I., Friedberg, I., Osterman, A., Godzik, A., Hunter, T., Dixon, J., and Mustelin, T. (2004). Protein tyrosine phosphatases in the human genome. Cell 117 699–711. - PubMed
-
- Baunsgaard, L., Lütken, H., Mikkelsen, R., Glaring, M.A., Pham, T.T., and Blennow, A. (2005). A novel isoform of glucan, water dikinase phosphorylates pre-phosphorylated α-glucans and is involved in starch degradation in Arabidopsis. Plant J. 41 595–605. - PubMed
-
- Blennow, A., Nielsen, T.H., Baunsgaard, L., Mikkelsen, R., and Engelsen, S.B. (2002). Starch phosphorylation: A new front line in starch research. Trends Plant Sci. 7 445–450. - PubMed
-
- Delatte, T., Umhang, M., Trevisan, M., Eicke, S., Thorneycroft, D., Smith, S.M., and Zeeman, S.C. (2006). Evidence for distinct mechanisms of starch granule breakdown in plants. J. Biol. Chem. 281 12050–12059. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- BBS/E/J/00000020/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- P20 RR020171/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- BBS/B/11877/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- R00 NS061803/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- BB/C513542/1/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

