Clinicopathologic features of CDK6 translocation-associated B-cell lymphoproliferative disorders
- PMID: 19145199
- PMCID: PMC2674112
- DOI: 10.1097/PAS.0b013e3181934244
Clinicopathologic features of CDK6 translocation-associated B-cell lymphoproliferative disorders
Abstract
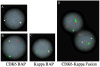
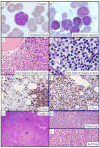
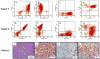
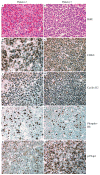
Cyclin-dependent protein kinase 6 (CDK6), in cooperation with cyclin Ds, drives cell cycle progression from G1 to S phase through phosphorylation and subsequent inactivation of retinoblastoma 1 protein. Alteration of this pathway results in both nonhematologic and hematologic malignancies, which include a small subset of B-cell lymphoproliferative disorders (BLPDs). We identified 5 cases of BLPD that carried CDK6 chromosomal translocations and characterized their clinical, pathologic, immunophenotypic, and genetic features. Common clinical characteristics included marked neoplastic lymphocytosis, systemic lymphadenopathy, splenomegaly, and bone marrow involvement. Three patients were diagnosed with low-grade B-cell lymphoma and had an indolent clinical course, and 2 patients (one who transformed to large B-cell lymphoma, and the other who was initially diagnosed with a high-grade B-cell lymphoma) had an aggressive clinical course. Immunophenotypically, the neoplastic B cells expressed CD5, CDK6, and cytoplasmic retinoblastoma 1 protein in all cases, expressed phospho-RB, p27kip1, and cyclin D2 in most cases, and uniformly lacked expression of all other cyclins. In 4 cases, the CDK6 translocation partner was kappa immunoglobulin light-chain gene; and in the fifth case, the CDK6 translocation partner was unknown. These distinct clinicopathologic and cytogenetic features distinguish the CDK6 translocation-associated BLPDs (CDK6-BLPDs) from other mature B-cell lymphomas.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Clinical and biological features of B-cell neoplasms with CDK6 translocations: an association with a subgroup of splenic marginal zone lymphomas displaying frequent CD5 expression, prolymphocytic cells, and TP53 abnormalities.Br J Haematol. 2021 Apr;193(1):72-82. doi: 10.1111/bjh.17141. Epub 2020 Dec 13. Br J Haematol. 2021. PMID: 33314017
-
Molecular characterization of a t(2;7) translocation linking CDK6 to the IGK locus in CD5(-) monoclonal B-cell lymphocytosis.Cancer Genet. 2011 May;204(5):260-4. doi: 10.1016/j.cancergen.2011.03.004. Cancer Genet. 2011. PMID: 21665179
-
Translocation t(2;7)(p11;q21) associated with the CDK6/IGK rearrangement is a rare but recurrent abnormality in B-cell lymphoproliferative malignancies.Cancer Genet. 2014 Mar;207(3):83-6. doi: 10.1016/j.cancergen.2014.02.009. Epub 2014 Feb 28. Cancer Genet. 2014. PMID: 24726269
-
Lymphoplasmacytic lymphoma/immunocytoma: towards a disease-targeted treatment?J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2001 Sep;20(3):351-8. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2001. PMID: 11718214 Review.
-
A translocation t(2;14)(p11.2;q32) involving rearrangements of immunoglobulin heavy chain and kappa light chain genes in B-cell lymphoma.Leuk Lymphoma. 2015;56(10):2992-4. doi: 10.3109/10428194.2015.1018249. Epub 2015 May 12. Leuk Lymphoma. 2015. PMID: 25682965 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
The role of CDK6 in cancer.Int J Cancer. 2020 Dec 1;147(11):2988-2995. doi: 10.1002/ijc.33054. Epub 2020 May 30. Int J Cancer. 2020. PMID: 32406095 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A kinase-independent function of CDK6 links the cell cycle to tumor angiogenesis.Cancer Cell. 2013 Aug 12;24(2):167-81. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2013.07.012. Cancer Cell. 2013. PMID: 23948297 Free PMC article.
-
Investigating the Mechanism of Inhibition of Cyclin-Dependent Kinase 6 Inhibitory Potential by Selonsertib: Newer Insights Into Drug Repurposing.Front Oncol. 2022 May 26;12:865454. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.865454. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35720007 Free PMC article.
-
Defining the borders of splenic marginal zone lymphoma: a multiparameter study.Hum Pathol. 2010 Apr;41(4):540-51. doi: 10.1016/j.humpath.2009.09.007. Epub 2009 Dec 11. Hum Pathol. 2010. PMID: 20004934 Free PMC article.
-
Cdc6 protein activates p27KIP1-bound Cdk2 protein only after the bound p27 protein undergoes C-terminal phosphorylation.J Biol Chem. 2012 Feb 24;287(9):6275-83. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.318295. Epub 2012 Jan 5. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22223646 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Andersen CL, Gruszka-Westwood A, Atkinson S, et al. Recurrent genomic imbalances in B-cell splenic marginal-zone lymphoma revealed by comparative genomic hybridization. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 2005;156:122–128. - PubMed
-
- Bassan R, Amaru R, Rambaldi A, et al. The natural history of monoclonal villous lymphocytosis: a chronic lymphoproliferative disorder of CD11c+ B cells. Leuk Lymphoma. 1996;21:181–183. - PubMed
-
- Bassan R, Neonato MG, Abbate M, et al. Monoclonal lymphocytosis with villous lymphocytes: a chronic lymphoproliferative disease of CD11c+ B-cells. Leukemia. 1991;5:799–806. - PubMed
-
- Bates S, Parry D, Bonetta L, et al. Absence of cyclin D/cdk complexes in cells lacking functional retinoblastoma protein. Oncogene. 1994;9:1633–1640. - PubMed
-
- Bell ND, King JA, Kusyk C, et al. CD5 negative diffuse mantle cell lymphoma with splenomegaly and bone marrow involvement. South Med J. 1998;91:584–587. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

