Effect of gap junction blocker beta-glycyrrhetinic acid on taste disk cells in frog
- PMID: 19145483
- PMCID: PMC11505803
- DOI: 10.1007/s10571-008-9342-6
Effect of gap junction blocker beta-glycyrrhetinic acid on taste disk cells in frog
Abstract
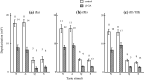
A gap junction blocker, 18beta-glycyrrhetinic acid (beta-GA), increased the membrane resistance of Ia, Ib and II/III cells of frog taste disk by 50, 160, and 300 M Omega, respectively, by blocking the gap junction channels and hemichannels. The amplitudes of gustatory depolarizing potentials in the disk cells for 4 basic taste stimuli were reduced to 40-60% after intravenous injection of beta-GA at 1.0 mg/kg. beta-GA of 1.0 mg/kg did not affect the resting potentials and the reversal potentials for tastant-induced depolarizing potentials in any taste disk cells. The percentage of cells responding to each of 4 basic taste stimuli and varying numbers of 4 taste qualities did not differ between control and beta-GA-treated taste disk cells. This implies that gustatory depolarizing response profiles for 4 basic taste stimuli were very similar in control and beta-GA-treated taste disk cells. It is concluded that beta-GA at 1.0 mg/kg reduced the amplitude of gustatory depolarizing potentials in taste disk cells by strongly blocking depolarizing currents flowing through the gap junction channels and hemichannels, but probably weakly affected the gustatory transduction mechanisms for 4 taste stimuli.
Figures









References
-
- Böhmer C, Kirschner U, Wehner F (2001) 18-β-glycyrrhetinic acid (BGA) as an electrical uncoupler for intracellular recordings in confluent monolayer cultures. Pflugers Arch 442:688–692. doi:10.1007/s004240100588 - PubMed
-
- Davidson JS, Baumgarten IM (1988) Glycyrrhetinic acid derivatives: a novel class of inhibitors of gap-junctional intercellular communication. Structure-activity relationships. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 246:1104–1107 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

