The role of insulin-like growth factor-I and its binding proteins in glucose homeostasis and type 2 diabetes
- PMID: 19145587
- PMCID: PMC4153414
- DOI: 10.1002/dmrr.919
The role of insulin-like growth factor-I and its binding proteins in glucose homeostasis and type 2 diabetes
Abstract
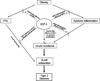
This review addresses the possible role of the insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-axis in normal glucose homoeostasis and in the etiopathogenesis of type 2 diabetes. IGF-I, a peptide hormone, shares amino acid sequence homology with insulin and has insulin-like activity; most notably, the promotion of glucose uptake by peripheral tissues. Type 2 diabetes as well as pre-diabetic states, including impaired fasting glucose and impaired glucose tolerance, are associated cross-sectionally with altered circulating levels of IGF-I and its binding proteins (IGFBPs). Administration of recombinant human IGF-I has been reported to improve insulin sensitivity in healthy individuals as well as in patients with insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. Further, IGF-I may have beneficial effects on systemic inflammation, a risk factor for type 2 diabetes, and on pancreatic beta-cell mass and function. There is considerable inter-individual heterogeneity in endogenous levels of IGF-I and its binding proteins; however, the relationship between these variations and the risk of developing type 2 diabetes has not been extensively investigated. Large prospective studies are required to evaluate this association.
Copyright 2009 John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Figures
References
-
- Le Roith D. Seminars in medicine of the Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center. Insulin-like growth factors. N Engl J Med. 1997;336:633–640. - PubMed
-
- Froesch ER, Schmid C, Schwander J, Zapf J. Actions of insulinlike growth factors. Annu Rev Physiol. 1985;47:443–467. - PubMed
-
- Rosenfeld RG, Hwa V, Wilson E, Plymate SR, Oh Y. The insulin-like growth factor-binding protein superfamily. Growth Horm IGF Res. 2000;10(Suppl. A):S16–S17. - PubMed
-
- LeRoith D, Werner H, Beitner-Johnson D, Roberts CT., Jr Molecular and cellular aspects of the insulin-like growth factor I receptor. Endocr Rev. 1995;16:143–163. - PubMed
-
- Jenkins P, Bustin S. Evidence for a link between IGF-I and cancer 10.1530/eje.0.151S017. Eur J Endocrinol. 2004;151:S17–S22. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical