MicroRNA expression in response to murine myocardial infarction: miR-21 regulates fibroblast metalloprotease-2 via phosphatase and tensin homologue
- PMID: 19147652
- PMCID: PMC2652741
- DOI: 10.1093/cvr/cvp015
MicroRNA expression in response to murine myocardial infarction: miR-21 regulates fibroblast metalloprotease-2 via phosphatase and tensin homologue
Abstract
Aims: MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are small non-coding RNAs that regulate gene expression at the post-transcriptional level by either degradation or translational repression of a target mRNA. Encoded in the genome of most eukaryotes, miRNAs have been proposed to regulate specifically up to 90% of human genes through a process known as miRNA-guided RNA silencing. For the first time, we sought to test how myocardial ischaemia-reperfusion (IR) changes miR expression.
Methods and results: Following 2 and 7 h of IR or sham operation, myocardial tissue was collected and subjected to miRNA expression profiling and quantification using a Bioarray system that screens for human-, mice-, rat-, and Ambi-miR. Data mining and differential analyses resulted in 13 miRs that were up-regulated on day 2, 9 miRs that were up-regulated on day 7, and 6 miRs that were down-regulated on day 7 post-IR. Results randomly selected from expression profiling were validated using real-time PCR. Tissue elements laser-captured from the infarct site showed marked induction of miR-21. In situ hybridization studies using locked nucleic acid miR-21-specific probe identified that IR-inducible miR-21 was specifically localized in the infarct region of the IR heart. Immunohistochemistry data show that cardiac fibroblasts (CFs) are the major cell type in the infarct zone. Studies with isolated CFs demonstrated that phosphatase and tensin homologue (PTEN) is a direct target of miR-21. Modulation of miR-21 regulated expression of matrix metalloprotease-2 (MMP-2) via a PTEN pathway. Finally, we noted a marked decrease in PTEN expression in the infarct zone. This decrease was associated with increased MMP-2 expression in the infarct area.
Conclusion: This work constitutes the first report describing changes in miR expression in response to IR in the mouse heart, showing that miR-21 regulates MMP-2 expression in CFs of the infarct zone via a PTEN pathway.
Figures
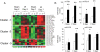

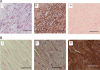



Comment in
-
MiRNA-21: a key to controlling the cardiac fibroblast compartment?Cardiovasc Res. 2009 Apr 1;82(1):1-3. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvp058. Epub 2009 Feb 12. Cardiovasc Res. 2009. PMID: 19213759 No abstract available.
-
miR-21: a central regulator of fibrosis not only in the broken heart.Cardiovasc Res. 2012 Nov 1;96(2):227-9; discussion 230-3. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvs200. Epub 2012 Aug 9. Cardiovasc Res. 2012. PMID: 22878017 No abstract available.
References
-
- Rajasingh J, Bord E, Hamada H, Lambers E, Qin G, Losordo DW, et al. STAT3-dependent mouse embryonic stem cell differentiation into cardiomyocytes: analysis of molecular signaling and therapeutic efficacy of cardiomyocyte precommitted mES transplantation in a mouse model of myocardial infarction. Circ Res. 2007;101:910–918. - PubMed
-
- Shilo S, Roy S, Khanna S, Sen CK. Evidence for the involvement of miRNA in redox regulated angiogenic response of human microvascular endothelial cells. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2008;28:471–477. - PubMed
-
- Roy S, Khanna S, Bickerstaff AA, Subramanian SV, Atalay M, Bierl M, et al. Oxygen sensing by primary cardiac fibroblasts: a key role of p21(Waf1/Cip1/Sdi1) Circ Res. 2003;92:264–271. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

