Mitochondrial mutations contribute to HIF1alpha accumulation via increased reactive oxygen species and up-regulated pyruvate dehydrogenease kinase 2 in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma
- PMID: 19147752
- PMCID: PMC2729126
- DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-08-0930
Mitochondrial mutations contribute to HIF1alpha accumulation via increased reactive oxygen species and up-regulated pyruvate dehydrogenease kinase 2 in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma
Abstract
Purpose: Mitochondrial mutations have been identified in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC), but the pathways by which phenotypic effects of these mutations are exerted remain unclear. Previously, we found that mitochondrial ND2 mutations in primary HNSCC increased reactive oxygen species (ROS) and conferred an aerobic, glycolytic phenotype with HIF1alpha accumulation and increased cell growth. The purpose of the present study was to examine the pathways relating these alterations.
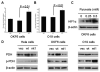
Experimental design: Mitochondrial mutant and wild-type ND2 constructs were transfected into oral keratinocyte immortal cell line OKF6 and head and neck cancer cell line JHU-O19 and established transfectants. The protein levels of HIF1alpha, pyruvate dehydrogenease (PDH), phosphorylated PDH, and pyruvate dehydrogenease kinase 2 (PDK2), together with ROS generation, were compared between the mutant and the wild type. Meanwhile, the effects of small molecule inhibitors targeting PDK2 and mitochondria-targeted catalase were evaluated on the ND2 mutant transfectants.
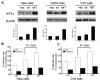
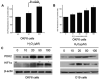
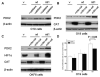
Results: We determined that ND2 mutant down-regulated PDH expression via up-regulated PDK2, with an increase in phosphorylated PDH. Inhibition of PDK2 with dichloroacetate decreased HIF1alpha accumulation and reduced cell growth. Extracellular treatment with hydrogen peroxide, a ROS mimic, increased PDK2 expression and HIF1alpha expression, and introduction of mitochondria-targeted catalase decreased mitochondrial mutation-mediated PDK2 and HIF1alpha expression and suppressed cell growth.
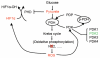
Conclusions: Our findings suggest that mitochondrial ND2 mutation contributes to HIF1alpha accumulation via increased ROS production, up-regulation of PDK2, attenuating PDH activity, thereby increasing pyruvate, resulting in HIF1alpha stabilization. This may provide insight into a potential mechanism, by which mitochondrial mutations contribute to HNSCC development.
Figures

References
-
- Wallace DC. Mitochondrial diseases in man and mouse. Science. 1999;283:1482–8. - PubMed
-
- Jiang WW, Califano J. Mitochondrial mutations and nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Cancer Biol Ther. 2004;3:1275–6. - PubMed
-
- Chatterjee A, Mambo E, Sidransky D. Mitochondrial DNA mutations in human cancer. Oncogene. 2006;25:4663–74. - PubMed
-
- Mithani SK, Taube JM, Zhou S, et al. Mitochondrial mutations are a late event in the progression of head and neck squamous cell cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2007;13:4331–5. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

