Krüppel-like factor 4 regulates adaptive expression of the zinc transporter Zip4 in mouse small intestine
- PMID: 19147802
- PMCID: PMC2660179
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpgi.90568.2008
Krüppel-like factor 4 regulates adaptive expression of the zinc transporter Zip4 in mouse small intestine
Erratum in
- Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2009 Jun;296(6):G1391
Abstract
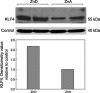
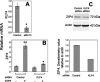
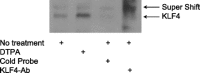
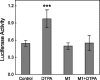
Epithelial cells of the small intestine are the site of zinc absorption. Intestinal uptake of zinc is inversely proportional to the dietary supply of this essential micronutrient. The mechanism responsible for this adaptive differential in apical zinc transport is not known. The zinc transporter Zip4 (Slc39a4) is essential for adequate enteric zinc uptake. In mice, Zip4 expression is upregulated at low zinc intakes with a concomitant ZIP4 localization to the apical enterocyte plasma membrane. With the present experiments, we show that the zinc finger transcription factor Krüppel-like factor 4 (KLF4), produced in high abundance in the intestine, is expressed at elevated levels in mice fed a low-zinc diet. In the murine intestinal epithelial cell (IEC) line MODE-K, zinc depletion of culture medium with cell-permeant and cell-impermeant chelators increased Zip4 and Klf4 mRNA and Zip4 heterogeneous nuclear RNA expression. Zinc depletion led to increased KLF4 in nuclear extracts. Knockdown of KLF4 using small interfering RNA transfection drastically limited ZIP4 induction upon zinc depletion and reduced 65Zn uptake by depleted IECs. EMSAs with nuclear extracts of IECs showed KLF4 binding to cis elements of the mouse Zip4 promoter, with increased binding under zinc-limited conditions. Reporter constructs with the Zip4 promoter and mutation studies further demonstrated that Zip4 is regulated through a KLF4 response element. These data from experiments with mice and murine IECs demonstrate that KLF4 is induced during zinc restriction and is a transcription factor involved in adaptive regulation of the zinc transporter ZIP4.
Figures





References
-
- Bhardhani MS, Borojevic R, Basak S, Ho E, Zhou P, Croitoru K. IL-10 protects mouse intestinal epithelial cells from Fas-induced apoptosis via modulating Fas expression and altering caspase-8 and FLIP expression. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 291: G820–G829, 2006 - PubMed
-
- Blanchard RK, Cousins RJ. Regulation of intestinal gene expression by dietary zinc: induction of urogyanylin mRNA by zinc deficiency. J Nutr 130: 1393S–1398S, 2000 - PubMed
-
- Cui L, Blanchard RK, Cousins RJ. The permissive effect of zinc deficiency on urogyanylin and inducible nitric oxide synthase gene upregulation in rat intestine induced by interleukin 1α is rapidly reversed by zinc repletion. J Nutr 133: 51–56, 2003 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

