IL-4/IL-13-dependent alternative activation of macrophages but not microglial cells is associated with uncontrolled cerebral cryptococcosis
- PMID: 19147811
- PMCID: PMC2630557
- DOI: 10.2353/ajpath.2009.080598
IL-4/IL-13-dependent alternative activation of macrophages but not microglial cells is associated with uncontrolled cerebral cryptococcosis
Abstract
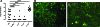
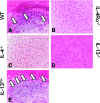
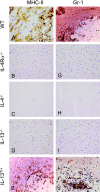
Both interleukin (IL)-4- and IL-13-dependent Th2-mediated immune mechanisms exacerbate murine Cryptococcus neoformans-induced bronchopulmonary disease. To study the roles of IL-4 and IL-13 in cerebral cryptococcosis, IL-4 receptor alpha-deficient (IL-4Ralpha(-/-)), IL-4-deficient (IL-4(-/-)), IL-13-deficient (IL-13(-/-)), IL-13 transgenic (IL-13(T/+)), and wild-type mice were infected intranasally. IL-13(T/+) mice displayed a higher fungal brain burden than wild-type mice, whereas the brain burdens of IL-4Ralpha(-/-), IL-4(-/-), and IL-13(-/-) mice were significantly lower as compared with wild-type mice. On infection, 68% of wild-type mice and 88% of IL-13-overexpressing IL-13(T/+) mice developed significant cerebral lesions. In contrast, only a few IL-4Ralpha(-/-), IL-4(-/-), and IL-13(-/-) mice had small lesions in their brains. Furthermore, IL-13(T/+) mice harbored large pseudocystic lesions in the central nervous system parenchyma, bordered by voluminous foamy alternatively activated macrophages (aaMphs) that contained intracellular cryptococci, without significant microglial activation. In wild-type mice, aaMphs tightly bordered pseudocystic lesions as well, and these mice, in addition, showed microglial cell activation. Interestingly, in resistant IL-4(-/-), IL-13(-/-), and IL-4Ralpha(-/-) mice, no aaMphs were discernible. Microglial cells of all mouse genotypes neither internalized cryptococci nor expressed markers of alternative activation, although they displayed similar IL-4Ralpha expression levels as macrophages. These data provide the first evidence of the development of aaMphs in a central nervous system infectious disease model, pointing to distinct roles of macrophages versus microglial cells in the central nervous system immune response against C. neoformans.
Figures




References
-
- Lortholary O, Nunez H, Brauner MW, Dromer F. Pulmonary cryptococcosis. Semin Respir Crit Care Med. 2004;25:145–157. - PubMed
-
- Malik R, Krockenberger MB, Cross G, Doneley R, Madill DN, Black D, McWhirter P, Rozenwax A, Rose K, Alley M, Forshaw D, Russell-Brown I, Johnstone AC, Martin P, O'Brien CR, Love DN. Avian cryptococcosis. Med Mycol. 2003;41:115–124. - PubMed
-
- McAdams HP, Rosado-de-Christenson ML, Lesar M, Templeton PA, Moran CA. Thoracic mycoses from endemic fungi: radiologic-pathologic correlation. Radiographics. 1995;15:255–270. - PubMed
-
- McAdams HP, Rosado-de-Christenson ML, Templeton PA, Lesar M, Moran CA. Thoracic mycoses from opportunistic fungi: radiologic-pathologic correlation. Radiographics. 1995;15:271–286. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

