Single-camera sequential-scan-based polarization-sensitive SDOCT for retinal imaging
- PMID: 19148256
- PMCID: PMC2756508
- DOI: 10.1364/ol.34.000205
Single-camera sequential-scan-based polarization-sensitive SDOCT for retinal imaging
Abstract
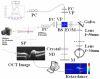
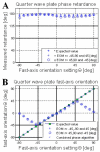
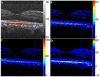
A single-camera, high-speed, polarization-sensitive, spectral-domain optical-coherence-tomography system was developed to measure the polarization properties of the in vivo human retina. A novel phase-unwrapping method in birefringent media is described to extract the total reflectivity, accumulative retardance, and fast-axis orientation from a specially designed sequence of polarization states incident on the sample. A quarter-wave plate was employed to test the performance of the system. The average error and standard deviation of retardation measurements were 3.2 degrees and 2.3 degrees , respectively, and of the fast-axis orientation 1.2 degrees and 0.7 degrees over the range of 0 degrees -180 degrees . The depolarization properties of the retinal pigment epithelium were clearly observed in both retardance and fast-axis orientation image. A normalized standard deviation of the retardance and of the fast-axis orientation is introduced to segment the polarization-scrambling layer of the retinal pigment epithelium.
Figures
References
-
- Hee MR, Huang D, Swanson EA, Fujimoto JG. J. Opt. Soc. Am. B. 1992;9:903.
-
- de Boer JF, Milner TE, van Gemert MJC, Nelson JS. Opt. Lett. 1997;22:934. - PubMed
-
- de Boer JF, Srinivas SM, Malekafzali A, Chen Z, Nelson JS. Opt. Express. 1998;3:212. - PubMed
-
- Jiao S, Yu W, Stoica G, Wang LV. Opt. Lett. 2003;28:1206. - PubMed
-
- Pircher M, Goetzinger E, Leitgeb R, Hitzenberger CK. Med. Biol. 2004;49:4. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

