Lasting epigenetic influence of early-life adversity on the BDNF gene
- PMID: 19150054
- PMCID: PMC3056389
- DOI: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2008.11.028
Lasting epigenetic influence of early-life adversity on the BDNF gene
Abstract
Background: Childhood maltreatment and early trauma leave lasting imprints on neural mechanisms of cognition and emotion. With a rat model of infant maltreatment by a caregiver, we investigated whether early-life adversity leaves lasting epigenetic marks at the brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) gene in the central nervous system.
Methods: During the first postnatal week, we exposed infant rats to stressed caretakers that predominately displayed abusive behaviors. We then assessed DNA methylation patterns and gene expression throughout the life span as well as DNA methylation patterns in the next generation of infants.
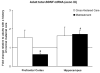
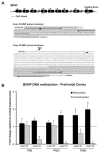
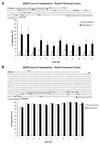
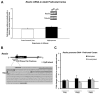
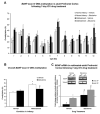
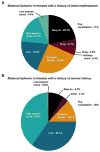
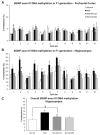
Results: Early maltreatment produced persisting changes in methylation of BDNF DNA that caused altered BDNF gene expression in the adult prefrontal cortex. Furthermore, we observed altered BDNF DNA methylation in offspring of females that had previously experienced the maltreatment regimen.
Conclusions: These results highlight an epigenetic molecular mechanism potentially underlying lifelong and transgenerational perpetuation of changes in gene expression and behavior incited by early abuse and neglect.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no biomedical financial interests or potential conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Cicchetti D, Toth SL. Child maltreatment. Ann Rev Clin Psychol. 2005;1:409–438. - PubMed
-
- De Bellis MD. The psychobiology of neglect. Child Maltreatment. 2005;10:150–172. - PubMed
-
- Lee V, Hoaken PN. Cognition, emotion, and neurobiological development: mediating the relation between maltreatment and aggression. Child Maltreatment. 2007;12:281–298. - PubMed
-
- Kaffman A, Meaney MJ. Neurodevelopmental sequelae of postnatal maternal care in rodents: clinical and research implications of molecular insights. J Child Psychol Psychiatry. 2007;48:224–244. - PubMed
-
- Fumagalli F, Molteni R, Racagni G, Riva MA. Stress during development: impact on neuroplasticity and relevance to psychopathology. Prog Neurobiol. 2007;81:197–217. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

