Phosphate-buffered saline-based nucleofection of primary endothelial cells
- PMID: 19150324
- PMCID: PMC2677097
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ab.2008.12.021
Phosphate-buffered saline-based nucleofection of primary endothelial cells
Abstract
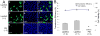
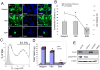
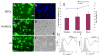
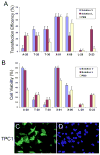
Although various nonviral transfection methods are available, cell toxicity, low transfection efficiency, and high cost remain hurdles for in vitro gene delivery in cultured primary endothelial cells. Recently, unprecedented transfection efficiency for primary endothelial cells has been achieved due to the newly developed nucleofection technology that uses a combination of novel electroporation condition and specific buffer components that stabilize the cells in the electrical field. Despite superior transfection efficiency and cell viability, high cost of the technology has discouraged cardiovascular researchers from liberally adopting this new technology. Here we report that a phosphate-buffered saline (PBS)-based nucleofection method can be used for efficient gene delivery into primary endothelial cells and other types of cells. Comparative analyses of transfection efficiency and cell viability for primary arterial, venous, microvascular, and lymphatic endothelial cells were performed using PBS. Compared with the commercial buffers, PBS can support equally remarkable nucleofection efficiency to both primary and nonprimary cells. Moreover, PBS-mediated nucleofection of small interfering RNA (siRNA) showed more than 90% knockdown of the expression of target genes in primary endothelial cells. We demonstrate that PBS can be an unprecedented economical alternative to the high-cost buffers or nucleofection of various primary and nonprimary cells.
Figures
References
-
- Ear T, Giguere P, Fleury A, Stankova J, Payet MD, Dupuis G. High efficiency transient transfection of genes in human umbilical vein endothelial cells by electroporation. J Immunol Methods. 2001 Nov 1;257(1–2):41–9. - PubMed
-
- Kotnis RA, Thompson MM, Eady SL, Budd JS, Bell PR, James RF. Optimisation of gene transfer into vascular endothelial cells using electroporation. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 1995 Jan;9(1):71–9. - PubMed
-
- Nathwani AC, Gale KM, Pemberton KD, Crossman DC, Tuddenham EG, McVey JH. Efficient gene transfer into human umbilical vein endothelial cells allows functional analysis of the human tissue factor gene promoter. Br J Haematol. 1994 Sep;88(1):122–8. - PubMed
-
- Sipehia R, Martucci G. High-efficiency transformation of human endothelial cells by Apo E-mediated transfection with plasmid DNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1995 Sep 5;214(1):206–11. - PubMed
-
- Tanner FC, Carr DP, Nabel GJ, Nabel EG. Transfection of human endothelial cells. Cardiovasc Res. 1997 Sep;35(3):522–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

