The role of membrane cholesterol in determining bile acid cytotoxicity and cytoprotection of ursodeoxycholic acid
- PMID: 19150330
- PMCID: PMC3805258
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2008.12.008
The role of membrane cholesterol in determining bile acid cytotoxicity and cytoprotection of ursodeoxycholic acid
Abstract
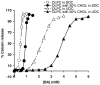
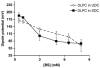
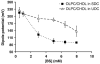
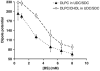
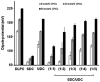
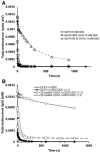
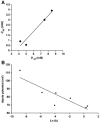
In cholestatic liver diseases, the ability of hydrophobic bile acids to damage membranes of hepatocytes/ductal cells contributes to their cytotoxicity. However, ursodeoxycholic acid (UDC), a hydrophilic bile acid, is used to treat cholestasis because it protects membranes. It has been well established that bile acids associate with and solubilize free cholesterol (CHOL) contained within the lumen of the gallbladder because of their structural similarities. However, there is a lack of understanding of how membrane CHOL, which is a well-established membrane stabilizing agent, is involved in cytotoxicity of hydrophobic bile acids and the cytoprotective effect of UDC. We utilized phospholipid liposomes to examine the ability of membrane CHOL to influence toxicity of individual bile acids, such as UDC and the highly toxic sodium deoxycholate (SDC), as well as the cytoprotective mechanism of UDC against SDC-induced cytotoxicity by measuring membrane permeation and intramembrane dipole potential. The kinetics of bile acid solubilization of phosphatidylcholine liposomes containing various levels of CHOL was also characterized. It was found that the presence of CHOL in membranes significantly reduced the ability of bile acids to damage synthetic membranes. UDC effectively prevented damaging effects of SDC on synthetic membranes only in the presence of membrane CHOL, while UDC enhances the damaging effects of SDC in the absence of CHOL. This further demonstrates that the cytoprotective effects of UDC depend upon the level of CHOL in the lipid membrane. Thus, changes in cell membrane composition, such as CHOL content, potentially influence the efficacy of UDC as the primary drug used to treat cholestasis.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Effect of some sulfonate analogues of ursodeoxycholic acid on biliary lipid secretion in the rat.J Lipid Res. 1996 Jun;37(6):1181-8. J Lipid Res. 1996. PMID: 8808752
-
Feeding diets containing 2% cheno- or urso-deoxycholic acid or cholestyramine to rats for two weeks alters intestinal morphology and bile acid absorption.Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1991 May;69(5):592-8. doi: 10.1139/y91-087. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1991. PMID: 1863909
-
Influence of oral treatment with ursodeoxycholic and tauroursodeoxycholic acids on estrogen-induced cholestasis in rats: effects on bile formation and liver plasma membranes.Liver. 1993 Aug;13(4):193-202. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0676.1993.tb00630.x. Liver. 1993. PMID: 8377596
-
[Bile acids and their therapeutic use in children].Arch Pediatr. 1995 Dec;2(12):1200-8. doi: 10.1016/0929-693x(96)89923-4. Arch Pediatr. 1995. PMID: 8548002 Review. French.
-
Molecular Mechanisms for Protection of Hepatocytes against Bile Salt Cytotoxicity.Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo). 2019;67(4):333-340. doi: 10.1248/cpb.c18-01029. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo). 2019. PMID: 30930437 Review.
Cited by
-
TUDCA modulates drug bioavailability to regulate resistance to acute ER stress in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Mol Biol Cell. 2025 Feb 1;36(2):ar13. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E24-04-0147. Epub 2024 Dec 11. Mol Biol Cell. 2025. PMID: 39661468 Free PMC article.
-
Snapshots of ABCG1 and ABCG5/G8: A Sterol's Journey to Cross the Cellular Membranes.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Dec 28;24(1):484. doi: 10.3390/ijms24010484. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36613930 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tauroursodeoxycholic acid inhibits experimental colitis by preventing early intestinal epithelial cell death.Lab Invest. 2014 Dec;94(12):1419-30. doi: 10.1038/labinvest.2014.117. Epub 2014 Oct 13. Lab Invest. 2014. PMID: 25310532
-
Periductal bile acid exposure causes cholangiocyte injury and fibrosis.PLoS One. 2022 Mar 16;17(3):e0265418. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0265418. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 35294492 Free PMC article.
-
Differential toxic effects of bile acid mixtures in isolated mitochondria and physiologically relevant HepaRG cells.Toxicol In Vitro. 2019 Dec;61:104595. doi: 10.1016/j.tiv.2019.104595. Epub 2019 Jul 6. Toxicol In Vitro. 2019. PMID: 31288073 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hofmann AF, Mysels KJ. Bile acid solubility and precipitation in vitro and in vivo: the role of conjugation, pH, and Ca2+ ions. J Lipid Res. 1992;33:617–626. - PubMed
-
- Shekels LL, Beste JE, Ho SB. Tauroursodeoxycholic acid protects in vitro models of human colonic cancer cells from cytotoxic effects of hydrophobic bile acids. J Lab Clin Med. 1996;127:57–66. - PubMed
-
- Paumgartner G, Beuers U. Ursodeoxycholic acid in cholestatic liver disease: mechanisms of action and therapeutic use revisited. Hepatology. 2002;36:525–531. - PubMed
-
- Guldutuna S, Zimmer G, Imhof M, Bhatti S, You T, Leuschner U. Molecular aspects of membrane stabilization by ursodeoxycholate [see comment] Gastroenterology. 1993;104:1736–1744. - PubMed
-
- Akare S, Martinez JD. Bile acid induces hydrophobicity-dependent membrane alterations. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2005;1735:59–67. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

