Neonatal pneumococcal conjugate vaccine immunization primes T cells for preferential Th2 cytokine expression: a randomized controlled trial in Papua New Guinea
- PMID: 19150378
- PMCID: PMC2697326
- DOI: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2008.12.046
Neonatal pneumococcal conjugate vaccine immunization primes T cells for preferential Th2 cytokine expression: a randomized controlled trial in Papua New Guinea
Abstract
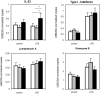
The effects of neonatal immunization with 7-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine (7vPCV) on development of T-cell memory and general immune maturation were studied in a cohort of Papua New Guinean newborns. Neonatal 7vPCV priming (followed by a dose at 1 and 2 months of age) was associated with enhanced Th2, but not Th1, cytokine responses to CRM(197) compared to 7vPCV at 1 and 2 months of age only. T cell responses to non-7vPCV vaccine antigens were similar in all groups, but TLR-mediated IL-6 and IL-10 responses were enhanced in 7vPCV vaccinated compared to controls. Neonatal 7vPCV vaccination primes T cell responses with a polarization towards Th2 with no bystander effects on other T cell responses.
Figures



References
-
- The Lancet. The world's forgotten children. Lancet. 2003;361(9351):1. - PubMed
-
- Rennels M.B., Edwards K.M., Keyserling H.L. Safety and immunogenicity of heptavalent pneumococcal vaccine conjugated to CRM197 in United States infants. Pediatrics. 1998;101(4 pt1):604–611. - PubMed
-
- Klugman K.P., Madhi S.A., Huebner R.E., Kohberger R., Mbelle N., Pierce N. A trial of a 9-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine in children with and those without HIV infection. N Engl J Med. 2003;349(14):1341–1348. - PubMed
-
- Schutze G.E., Tucker N.C., Mason E.O., Jr Impact of the conjugate pneumococcal vaccine in Arkansas. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2004;23(12):1125–1129. - PubMed
-
- Cutts F.T., Zaman S.M., Enwere G., Jaffar S., Levine O.S., Okoko J.B. Efficacy of nine-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine against pneumonia and invasive pneumococcal disease in The Gambia: randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet. 2005;365(9465):1139–1146. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

