A conserved salt bridge in the G loop of multiple protein kinases is important for catalysis and for in vivo Lyn function
- PMID: 19150426
- PMCID: PMC2683036
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2008.12.024
A conserved salt bridge in the G loop of multiple protein kinases is important for catalysis and for in vivo Lyn function
Abstract
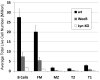
The glycine-rich G loop controls ATP binding and phosphate transfer in protein kinases. Here we show that the functions of Src family and Abl protein tyrosine kinases require an electrostatic interaction between oppositely charged amino acids within their G loops that is conserved in multiple other phylogenetically distinct protein kinases, from plants to humans. By limiting G loop flexibility, it controls ATP binding, catalysis, and inhibition by ATP-competitive compounds such as Imatinib. In WeeB mice, mutational disruption of the interaction results in expression of a Lyn protein with reduced catalytic activity, and in perturbed B cell receptor signaling. Like Lyn(-/-) mice, WeeB mice show profound defects in B cell development and function and succumb to autoimmune glomerulonephritis. This demonstrates the physiological importance of the conserved G loop salt bridge and at the same time distinguishes the in vivo requirement for the Lyn kinase activity from other potential functions of the protein.
Figures


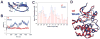


References
-
- Aimes RT, Hemmer W, Taylor SS. Serine-53 at the tip of the glycine-rich loop of cAMP-dependent protein kinase: role in catalysis, P-site specificity, and interaction with inhibitors. Biochemistry. 2000;39:8325–8332. - PubMed
-
- Allman D, Lindsley RC, DeMuth W, Rudd K, Shinton SA, Hardy RR. Resolution of three nonproliferative immature splenic B cell subsets reveals multiple selection points during peripheral B cell maturation. J Immunol. 2001;167:6834–6840. - PubMed
-
- Campbell KS. Signal transduction from the B cell antigen-receptor. Curr Opin Immunol. 1999;11:256–264. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

