Distinct requirements for the Rad32(Mre11) nuclease and Ctp1(CtIP) in the removal of covalently bound topoisomerase I and II from DNA
- PMID: 19150433
- PMCID: PMC2675033
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2008.11.021
Distinct requirements for the Rad32(Mre11) nuclease and Ctp1(CtIP) in the removal of covalently bound topoisomerase I and II from DNA
Abstract
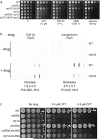
For a cancer cell to resist treatment with drugs that trap topoisomerases covalently on the DNA, the topoisomerase must be removed. In this study, we provide evidence that the Schizosaccharomyces pombe Rad32(Mre11) nuclease activity is involved in the removal of both Top2 from 5' DNA ends as well as Top1 from 3' ends in vivo. A ctp1(CtIP) deletion is defective for Top2 removal but overproficient for Top1 removal, suggesting that Ctp1(CtIP) plays distinct roles in removing topoisomerases from 5' and 3' DNA ends. Analysis of separation of function mutants suggests that MRN-dependent topoisomerase removal contributes significantly to resistance against topoisomerase-trapping drugs. This study has important implications for our understanding of the role of the MRN complex and CtIP in resistance of cells to a clinically important group of anticancer drugs.
Figures


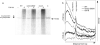
References
-
- Baldwin EL, Osheroff N. Etoposide, topoisomerase II and cancer. Curr Med Chem Anticancer Agents. 2005;5:363–72. - PubMed
-
- Champoux JJ. DNA TOPOISOMERASES: Structure, Function, and Mechanism. Annual Review of Biochemistry. 2001;70:369–413. - PubMed
-
- Connelly JC, de Leau ES, Leach DRF. Nucleolytic processing of a protein-bound DNA end by the E. coli SbcCD (MR) complex. DNA Repair (Amst.) 2003;2:795–807. - PubMed
-
- Connelly JC, Leach DRF. Repair of DNA Covalently Linked to Protein. Molecular Cell. 2004;13:307–316. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

