Potential mechanism of cell death in the developing rat brain induced by propofol anesthesia
- PMID: 19150648
- PMCID: PMC3886115
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ijdevneu.2008.12.005
Potential mechanism of cell death in the developing rat brain induced by propofol anesthesia
Erratum in
- Int J Dev Neurosci. 2010 Apr;28(2):225
Abstract
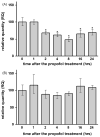
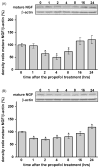
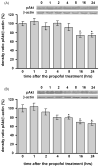
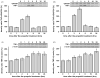
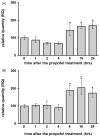
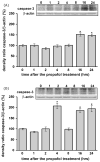
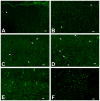
Commonly used general anesthetics can have adverse effects on the developing brain by triggering apoptotic neurodegeneration, as has been documented in the rat. The rational of our study was to examine the molecular mechanisms that contribute to the apoptotic action of propofol anesthesia in the brain of 7-day-old (P7) rats. The down-regulation of nerve growth factor (NGF) mRNA and protein expression in the cortex and thalamus at defined time points between 1 and 24h after the propofol treatment, as well as a decrease of phosphorylated Akt were observed. The extrinsic apoptotic pathway was induced by over-expression of tumor necrosis factor (TNF) which led to the activation of caspase-3 in both examined structures. Neurodegeneration was confirmed by Fluoro-Jade B staining. Our findings provide direct experimental evidence that the anesthetic dose (25mg/kg) of propofol induces complex changes that are accompanied by cell death in the cortex and thalamus of the developing rat brain.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Propofol-induced changes in neurotrophic signaling in the developing nervous system in vivo.PLoS One. 2012;7(4):e34396. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0034396. Epub 2012 Apr 4. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22496799 Free PMC article.
-
Propofol anesthesia induces proapoptotic tumor necrosis factor-α and pro-nerve growth factor signaling and prosurvival Akt and XIAP expression in neonatal rat brain.J Neurosci Res. 2014 Oct;92(10):1362-73. doi: 10.1002/jnr.23409. Epub 2014 May 14. J Neurosci Res. 2014. PMID: 24827783 Free PMC article.
-
Induction of TNF-α signaling cascade in neonatal rat brain during propofol anesthesia.Int J Dev Neurosci. 2015 Aug;44:22-32. doi: 10.1016/j.ijdevneu.2015.05.003. Epub 2015 May 14. Int J Dev Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 25980792
-
Regional and temporal profiles of calpain and caspase-3 activities in postnatal rat brain following repeated propofol administration.Dev Neurosci. 2010;32(4):288-301. doi: 10.1159/000316970. Epub 2010 Aug 12. Dev Neurosci. 2010. PMID: 20714114 Free PMC article.
-
Brain imaging in research on anesthetic mechanisms: studies with propofol.Prog Brain Res. 2005;150:245-50. doi: 10.1016/S0079-6123(05)50018-9. Prog Brain Res. 2005. PMID: 16186028 Review.
Cited by
-
Propofol-induced changes in neurotrophic signaling in the developing nervous system in vivo.PLoS One. 2012;7(4):e34396. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0034396. Epub 2012 Apr 4. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22496799 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of the neuropsychological mechanisms of 2,6-diisopropylphenol and N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor antagonist against electroconvulsive therapy-induced learning and memory impairment in depressed rats.Mol Med Rep. 2015 Sep;12(3):3297-3308. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2015.3803. Epub 2015 May 21. Mol Med Rep. 2015. PMID: 25998151 Free PMC article.
-
Propofol anesthesia induces proapoptotic tumor necrosis factor-α and pro-nerve growth factor signaling and prosurvival Akt and XIAP expression in neonatal rat brain.J Neurosci Res. 2014 Oct;92(10):1362-73. doi: 10.1002/jnr.23409. Epub 2014 May 14. J Neurosci Res. 2014. PMID: 24827783 Free PMC article.
-
Neonatal Propofol Anesthesia Changes Expression of Synaptic Plasticity Proteins and Increases Stereotypic and Anxyolitic Behavior in Adult Rats.Neurotox Res. 2017 Aug;32(2):247-263. doi: 10.1007/s12640-017-9730-0. Epub 2017 Apr 24. Neurotox Res. 2017. PMID: 28435999
-
Functional implications of an early exposure to general anesthesia: are we changing the behavior of our children?Mol Neurobiol. 2013 Oct;48(2):288-93. doi: 10.1007/s12035-013-8488-5. Epub 2013 Jul 3. Mol Neurobiol. 2013. PMID: 23821029 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Allegaert K, Peeters MY, Veresselt R, Tibboel D, Naulaers G, de Hoon JN, Knibbe CA. Inter-individual variability in propofol pharmacokinetics in preterm and term neonates. Br J Anaesth. 2007;99:864–870. - PubMed
-
- Angel A, LeBeau F. A comparison of the effects of propofol with other anaesthetic agents on the centripetal transmission of sensory information. Gen Pharmacol. 1992;23:945–963. - PubMed
-
- Barker V, Middleton G, Davey F, Davies AM. TNFα contributes to the death of NGF-dependent neurons during development. Nat Neurosci. 2001;4:1194–1198. - PubMed
-
- Baud V, Karin M. Signal transduction by tumor necrosis factor and its relatives. Trends Cell Biol. 2001;11:372–377. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

