Sensing chromosome bi-orientation by spatial separation of aurora B kinase from kinetochore substrates
- PMID: 19150808
- PMCID: PMC2713345
- DOI: 10.1126/science.1167000
Sensing chromosome bi-orientation by spatial separation of aurora B kinase from kinetochore substrates
Abstract
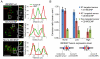
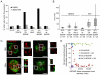
Successful cell division requires that chromosomes attach to opposite poles of the mitotic spindle (bi-orientation). Aurora B kinase regulates chromosome-spindle attachments by phosphorylating kinetochore substrates that bind microtubules. Centromere tension stabilizes bi-oriented attachments, but how physical forces are translated into signaling at individual centromeres is unknown. Using fluorescence resonance energy transfer-based biosensors to measure localized phosphorylation dynamics in living cells, we found that phosphorylation of an Aurora B substrate at the kinetochore depended on its distance from the kinase at the inner centromere. Furthermore, repositioning Aurora B closer to the kinetochore prevented stabilization of bi-oriented attachments and activated the spindle checkpoint. Thus, centromere tension can be sensed by increased spatial separation of Aurora B from kinetochore substrates, which reduces phosphorylation and stabilizes kinetochore microtubules.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

