A necessary role of miR-221 and miR-222 in vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation and neointimal hyperplasia
- PMID: 19150885
- PMCID: PMC2728290
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.108.185363
A necessary role of miR-221 and miR-222 in vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation and neointimal hyperplasia
Abstract
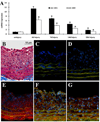
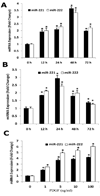
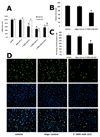
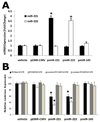
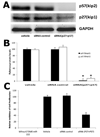
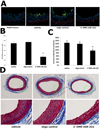
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) comprise a novel class of endogenous, small, noncoding RNAs that negatively regulate gene expression. Functionally, an individual miRNA is as important as a transcription factor because it is able to regulate the expression of its multiple target genes. Recently, miR-221 and miR-222 have been found to play a critical role in cancer cell proliferation. However, their roles in vascular smooth muscle cell (VSMC) biology are currently unknown. In the present study, the time course changes and cellular distribution of miR-221 and miR-222 expression were identified in rat carotid arteries after angioplasty, in which their expression was upregulated and localized in VSMCs in the injured vascular walls. In cultured VSMCs, miR-221 and miR-222 expression was increased by growth stimulators. Knockdown of miR-221 and miR-222 resulted in decreased VSMC proliferation in vitro. Using both gain-of-function and loss-of-function approaches, we found that p27(Kip1) and p57(Kip2) were 2 target genes that were involved in miR-221- and miR-222-mediated effect on VSMC growth. Finally, knockdown of miR-221 and miR-222 in rat carotid arteries suppressed VSMC proliferation in vivo and neointimal lesion formation after angioplasty. The results indicate that miR-221 and miR-222 are novel regulators for VSMC proliferation and neointimal hyperplasia. These findings may also represent promising therapeutic targets in proliferative vascular diseases.
Figures


Similar articles
-
MicroRNA-145, a novel smooth muscle cell phenotypic marker and modulator, controls vascular neointimal lesion formation.Circ Res. 2009 Jul 17;105(2):158-66. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.109.197517. Epub 2009 Jun 18. Circ Res. 2009. PMID: 19542014 Free PMC article.
-
S-phase kinase-associated protein-2 (Skp2) promotes vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation and neointima formation in vivo.J Vasc Surg. 2009 Nov;50(5):1135-42. doi: 10.1016/j.jvs.2009.07.066. J Vasc Surg. 2009. PMID: 19878790 Free PMC article.
-
Fibroblast Growth Factor 12 Is a Novel Regulator of Vascular Smooth Muscle Cell Plasticity and Fate.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2016 Sep;36(9):1928-36. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.116.308017. Epub 2016 Jul 28. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2016. PMID: 27470512
-
Role of specific microRNAs in regulation of vascular smooth muscle cell differentiation and the response to injury.J Cardiovasc Transl Res. 2010 Jun;3(3):246-50. doi: 10.1007/s12265-010-9163-0. J Cardiovasc Transl Res. 2010. PMID: 20543900 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNA-145 in vascular smooth muscle cell biology: a new therapeutic target for vascular disease.Cell Cycle. 2009 Nov 1;8(21):3469-73. doi: 10.4161/cc.8.21.9837. Epub 2009 Nov 17. Cell Cycle. 2009. PMID: 19829088 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Plasma Small Extracellular Vesicle-Carried miRNA-501-5p Promotes Vascular Smooth Muscle Cell Phenotypic Modulation-Mediated In-Stent Restenosis.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021 Apr 21;2021:6644970. doi: 10.1155/2021/6644970. eCollection 2021. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021. PMID: 33968296 Free PMC article.
-
The short and long of noncoding sequences in the control of vascular cell phenotypes.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2015 Sep;72(18):3457-88. doi: 10.1007/s00018-015-1936-9. Epub 2015 May 29. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2015. PMID: 26022065 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Elevation of miR-221 and -222 in the internal mammary arteries of diabetic subjects and normalization with metformin.Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2013 Jul 15;374(1-2):125-9. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2013.04.019. Epub 2013 May 3. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2013. PMID: 23648338 Free PMC article.
-
Human miR-221/222 in Physiological and Atherosclerotic Vascular Remodeling.Biomed Res Int. 2015;2015:354517. doi: 10.1155/2015/354517. Epub 2015 Jun 29. Biomed Res Int. 2015. PMID: 26221589 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Therapeutic implication of MicroRNA-320a antagonist in attenuating blood clots formed during venous thrombosis.J Thromb Thrombolysis. 2024 Apr;57(4):699-709. doi: 10.1007/s11239-024-02947-6. Epub 2024 Feb 23. J Thromb Thrombolysis. 2024. PMID: 38393674
References
-
- Ambros V. The functions of animal microRNAs. Nature. 2004;431:350–355. - PubMed
-
- Ambros V. MicroRNA pathways in flies and worms: growth, death, fat, stress, and timing. Cell. 2003;113:673–676. - PubMed
-
- Farh KK, Grimson A, Jan C, Lewis BP, Johnston WK, Lim LP, Burge CB, Bartel DP. The widespread impact of mammalian MicroRNAs on mRNA repression and evolution. Science. 2005;310:1817–1821. - PubMed
-
- Pasquinelli AE, Hunter S, Bracht J. MicroRNAs: a developing story. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2005;15:200–205. - PubMed
-
- Bartel DP. MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 2004;116:281–297. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

