Income-related health inequalities in Canada and the United States: a decomposition analysis
- PMID: 19150915
- PMCID: PMC2741511
- DOI: 10.2105/AJPH.2007.129361
Income-related health inequalities in Canada and the United States: a decomposition analysis
Abstract
Objectives: We examined income-related inequalities in self-reported health in the United States and Canada and the extent to which they are associated with individual-level risk factors and health care system characteristics.
Methods: We estimated income inequalities with concentration indexes and curves derived from comparable survey data from the 2002 to 2003 Joint Canada-US Survey of Health. Inequalities were then decomposed by regression and decomposition analysis to distinguish the contributions of various factors.
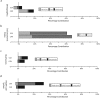
Results: The distribution of income accounted for close to half of income-related health inequalities in both the United States and Canada. Health care system factors (e.g., unmet needs and health insurance status) and risk factors (e.g., physical inactivity and obesity) contributed more to income-related health inequalities in the United States than to those in Canada.
Conclusions: Individual-level health risk factors and health care system characteristics have similar associations with health status in both countries, but they both are far more prevalent and much more concentrated among lower-income groups in the United States than in Canada.
Figures
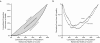
References
-
- Marmot M. Social determinants of health inequalities. Lancet 2005;365:1099–1104 - PubMed
-
- Marmot M, Feeney A. General explanations for social inequalities in health. IARC Sci Publ 1997;138:207–228 - PubMed
-
- Siddiqi A, Hertzman C. Towards an epidemiological understanding of the effects of long-term institutional changes on population health: a case study of Canada versus the USA. Soc Sci Med 2007;64:589–603 - PubMed
-
- Marmot M. Achieving health equity: from root causes to fair outcomes. Lancet 2007;370:1153–1163 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

