A critical role for the TIFY motif in repression of jasmonate signaling by a stabilized splice variant of the JASMONATE ZIM-domain protein JAZ10 in Arabidopsis
- PMID: 19151223
- PMCID: PMC2648087
- DOI: 10.1105/tpc.108.064097
A critical role for the TIFY motif in repression of jasmonate signaling by a stabilized splice variant of the JASMONATE ZIM-domain protein JAZ10 in Arabidopsis
Abstract
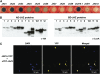
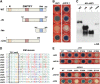
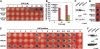
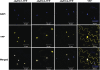
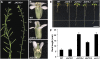
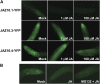
JASMONATE ZIM-domain (JAZ) proteins act as repressors of jasmonate (JA) signaling. Perception of bioactive JAs by the F-box protein CORONATINE INSENSITIVE1 (COI1) causes degradation of JAZs via the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway, which in turn activates the expression of genes involved in plant growth, development, and defense. JAZ proteins contain two highly conserved sequence regions: the Jas domain that interacts with COI1 to destabilize the repressor and the ZIM domain of unknown function. Here, we show that the conserved TIFY motif (TIFF/YXG) within the ZIM domain mediates homo- and heteromeric interactions between most Arabidopsis thaliana JAZs. We have also identified an alternatively spliced form (JAZ10.4) of JAZ10 that lacks the Jas domain and, as a consequence, is highly resistant to JA-induced degradation. Strong JA-insensitive phenotypes conferred by overexpression of JAZ10.4 were suppressed by mutations in the TIFY motif that block JAZ10.4-JAZ interactions. We conclude that JAZ10.4 functions to attenuate signal output in the presence of JA and further suggest that the dominant-negative action of this splice variant involves protein-protein interaction through the ZIM/TIFY domain. The ability of JAZ10.4 to interact with MYC2 is consistent with a model in which a JAZ10.4-containing protein complex directly represses the activity of transcription factors that promote expression of JA response genes.
Figures


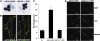
References
-
- Balbi, V., and Devoto, A. (2008). Jasmonate signalling network in Arabidopsis thaliana: Crucial regulatory nodes and new physiological scenarios. New Phytol. 177 301–318. - PubMed
-
- Barbazuk, W.B., Fu, Y., and McGinnis, K.M. (2008). Genome-wide analyses of alternative splicing in plants: Opportunities and challenges. Genome Res. 18 1381–1392. - PubMed
-
- Bove, J., Kim, C.Y., Gibson, C.A., and Assmann, S.M. (2008). Characterization of wound-responsive RNA-binding proteins and their splice variants in Arabidopsis. Plant Mol. Biol. 67 71–88. - PubMed
-
- Bracha-Drori, K., Shichrur, K., Katz, A., Oliva, M., Angelovici, R., Yalovsky, S., and Ohad, N. (2004). Detection of protein-protein interactions in plants using bimolecular fluorescence complementation. Plant J. 40 419–427. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

