KCNQ modulators reveal a key role for KCNQ potassium channels in regulating the tone of rat pulmonary artery smooth muscle
- PMID: 19151245
- PMCID: PMC2684066
- DOI: 10.1124/jpet.108.147785
KCNQ modulators reveal a key role for KCNQ potassium channels in regulating the tone of rat pulmonary artery smooth muscle
Abstract
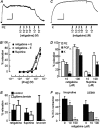
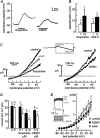
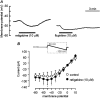
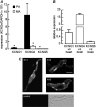
Potassium channels are central to the regulation of pulmonary vascular tone. The smooth muscle cells of pulmonary artery display a background K(+) conductance with biophysical properties resembling those of KCNQ (K(V)7) potassium channels. Therefore, we investigated the expression and functional role of KCNQ channels in pulmonary artery. The effects of selective KCNQ channel modulators were investigated on K(+) current and membrane potential in isolated pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells (PASMCs), on the tension developed by intact pulmonary arteries, and on pulmonary arterial pressure in isolated perfused lungs and in vivo. The KCNQ channel blockers, linopirdine and XE991 [10,10-bis(4-pyridinylmethyl)-9(10H)-anthracenone], inhibited the noninactivating background K(+) conductance in PASMCs and caused depolarization, vasoconstriction, and raised pulmonary arterial pressure without constricting several systemic arteries or raising systemic pressure. The KCNQ channel openers, retigabine and flupirtine, had the opposite effects. PASMCs were found to express KCNQ4 mRNA, at higher levels than mesenteric artery, along with smaller amounts of KCNQ1 and 5. It is concluded that KCNQ channels, most probably KCNQ4, make an important contribution to the regulation of pulmonary vascular tone, with a greater contribution in pulmonary compared with systemic vessels. The pulmonary vasoconstrictor effect of KCNQ blockers is a potentially serious side effect, but the pulmonary vasodilator effect of the openers may be useful in the treatment of pulmonary hypertension.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Pulmonary vasoconstrictor action of KCNQ potassium channel blockers.Respir Res. 2006 Feb 20;7(1):31. doi: 10.1186/1465-9921-7-31. Respir Res. 2006. PMID: 16504007 Free PMC article.
-
Vascular KCNQ potassium channels as novel targets for the control of mesenteric artery constriction by vasopressin, based on studies in single cells, pressurized arteries, and in vivo measurements of mesenteric vascular resistance.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2008 May;325(2):475-83. doi: 10.1124/jpet.107.135764. Epub 2008 Feb 13. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2008. PMID: 18272810 Free PMC article.
-
Role of KCNQ channels in skeletal muscle arteries and periadventitial vascular dysfunction.Hypertension. 2013 Jan;61(1):151-9. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.112.197566. Epub 2012 Nov 26. Hypertension. 2013. PMID: 23184384
-
Novel treatment strategies for smooth muscle disorders: Targeting Kv7 potassium channels.Pharmacol Ther. 2016 Sep;165:14-25. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2016.05.002. Epub 2016 May 11. Pharmacol Ther. 2016. PMID: 27179745 Review.
-
KCNQ potassium channels: new targets for pulmonary vasodilator drugs?Adv Exp Med Biol. 2010;661:405-17. doi: 10.1007/978-1-60761-500-2_26. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2010. PMID: 20204745 Review.
Cited by
-
Redox regulation of ion channels in the pulmonary circulation.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2015 Feb 20;22(6):465-85. doi: 10.1089/ars.2014.5899. Epub 2014 Jun 30. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2015. PMID: 24702125 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Functional effects of KCNQ K(+) channels in airway smooth muscle.Front Physiol. 2013 Oct 7;4:277. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2013.00277. eCollection 2013. Front Physiol. 2013. PMID: 24109455 Free PMC article.
-
KV7 channels contribute to paracrine, but not metabolic or ischemic, regulation of coronary vascular reactivity in swine.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2016 Mar 15;310(6):H693-704. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00688.2015. Epub 2016 Jan 29. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2016. PMID: 26825518 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacological dissection of K(v)7.1 channels in systemic and pulmonary arteries.Br J Pharmacol. 2012 Jun;166(4):1377-87. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2012.01863.x. Br J Pharmacol. 2012. PMID: 22251082 Free PMC article.
-
Involvement of butyrate in electrogenic K+ secretion in rat rectal colon.Pflugers Arch. 2019 Feb;471(2):313-327. doi: 10.1007/s00424-018-2208-y. Epub 2018 Sep 25. Pflugers Arch. 2019. PMID: 30250967 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Archer SL, Souil E, Dinh-Xuan AT, Schremmer B, Mercier JC, El Yaagoubi A, Nguyen-Huu L, Reeve HL, and Hampl V (1998) Molecular identification of the role of voltage-gated K+ channels, Kv1.5 and Kv2.1, in hypoxic pulmonary vasoconstriction and control of resting membrane potential in rat pulmonary artery myocytes. J Clin Invest 101 2319-2330. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Clapp LH, Davey R, and Gurney AM (1993) ATP-sensitive K+ channels mediate vasodilation produced by lemakalim in rabbit pulmonary artery. Am J Physiol 264 H1907-H1915. - PubMed
-
- Clapp LH and Gurney AM (1992) ATP-sensitive K+ channels regulate resting potential of pulmonary arterial smooth muscle cells. Am J Physiol 262 H916-H920. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

