Preclinical assessment of vernonia amygdalina leaf extracts as DNA damaging anti-cancer agent in the management of breast cancer
- PMID: 19151427
- PMCID: PMC3699992
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph5050337
Preclinical assessment of vernonia amygdalina leaf extracts as DNA damaging anti-cancer agent in the management of breast cancer
Abstract
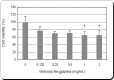
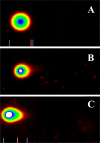
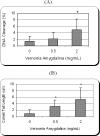
Breast cancer is the leading cause of death among women between 40 and 55 years of age and is the second overall cause of death among women. Fortunately, the mortality rate from breast cancer has decreased in recent years due to an increased emphasis on early detection and more effective treatments. Despite early detection, conventional and chemotherapeutic methods of treatment, about 7% of women still died every year. Hence, the aim of the present study was to assess the therapeutic efficacy of vernonia amygdalina (VA) leaf extracts as anti-cancer agent against human breast cancer in vitro using the MTT [3-(4, 5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide[ and alkaline single cell gel electrophoresis (Comet) assays, respectively. In this experiment, human breast adenocarcinoma (MCF-7) cells were treated with different doses of VA leaf extracts for 48 hours. Data obtained from the MTT assay showed that VA significantly ((P < 0.05) reduced the viability of MCF-7 cells in a dose-dependent manner upon 48 hours of exposure. Data generated from the comet assay also indicated a slight dose-dependent increase in DNA damage in MCF-7 cells associated with VA treatment. We observed a slight increase in comet tail-length, tail arm and tail moment, as well as in percentages of DNA cleavage at all doses tested, showing an evidence that VA-induced minimal genotoxic damage in MCF-7 cells. Taken together, our findings suggest that VA treatment moderately (P < 0.05) reduces cellular viability and induces minimal DNA damage in MCF-7 cells. These findings provide evidence that VA extracts represent a DNA-damaging anti-cancer agent against breast cancer and its mechanisms of action functions, at least in part, through minimal DNA damage and moderate toxicity in tumors cells.
Figures
References
-
- Ainslie JR. List of plants used in native medicine in Nigeria. Imperial Forestry Institute; Oxford, UK: 1973. p. 42.
-
- Burkill HM. The useful plants of West tropical Africa. 2d ed. Vol. 1 England: Royal Botanical Gardens; 1985. Kew.
-
- Izevbigie EB. Discovery of water-soluble anticancer agents (edotides) from a vegetable found in Benin City, Nigeria. Exp. Biol. Med. 2003;228:293–298. - PubMed
-
- Tadesse A, Gebre-Hiwot A, Asres K, Djote M, Frommel D. The in vitro activity of Vernonia amygdalina on Leishmania aethiopica. Ethiop. Med. J. 1993;31:183–189. - PubMed
-
- Hamowia AM, Saffaf AM. Pharmacological studies on Vernonia amygdalina (Del)and tithonia diversifolia (Gray) Vet. Med. J. 1994;2:91–97.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
