Intracellular NAD levels regulate tumor necrosis factor protein synthesis in a sirtuin-dependent manner
- PMID: 19151729
- PMCID: PMC2845476
- DOI: 10.1038/nm.1906
Intracellular NAD levels regulate tumor necrosis factor protein synthesis in a sirtuin-dependent manner
Abstract
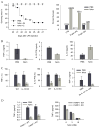
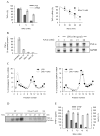
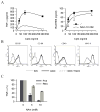
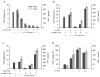
Tumor necrosis factor (TNF) synthesis is known to play a major part in numerous inflammatory disorders, and multiple transcriptional and post-transcriptional regulatory mechanisms have therefore evolved to dampen the production of this key proinflammatory cytokine. The high expression of nicotinamide phosphoribosyltransferase (Nampt), an enzyme involved in the nicotinamide-dependent NAD biosynthetic pathway, in cells of the immune system has led us to examine the potential relationship between NAD metabolism and inflammation. We show here that intracellular NAD concentration promotes TNF synthesis by activated immune cells. Using a positive screen, we have identified Sirt6, a member of the sirtuin family, as the NAD-dependent enzyme able to regulate TNF production by acting at a post-transcriptional step. These studies reveal a previously undescribed relationship between metabolism and the inflammatory response and identify Sirt6 and the nicotinamide-dependent NAD biosynthetic pathway as novel candidates for immunointervention in an inflammatory setting.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
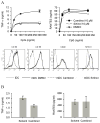
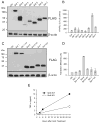
References
-
- Ziegler M. New functions of a long-known molecule. Emerging roles of NAD in cellular signaling. Eur J Biochem. 2000;267:1550–64. - PubMed
-
- Ame JC, Spenlehauer C, de Murcia G. The PARP superfamily. Bioessays. 2004;26:882–93. - PubMed
-
- Guarente L. Sirtuins as potential targets for metabolic syndrome. Nature. 2006;444:868–74. - PubMed
-
- Vaquero A, et al. Human SirT1 interacts with histone H1 and promotes formation of facultative heterochromatin. Mol Cell. 2004;16:93–105. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

