TNFalpha-induced macrophage death via caspase-dependent and independent pathways
- PMID: 19152111
- PMCID: PMC2692057
- DOI: 10.1007/s10495-009-0311-4
TNFalpha-induced macrophage death via caspase-dependent and independent pathways
Abstract
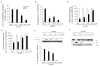
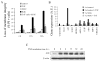
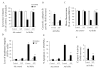
Macrophages are the principal source of TNFalpha, yet they are highly resistant to TNFalpha-mediated cell death. Previously, employing in vitro differentiated human macrophages, we showed that following the inhibition of NF-kappaB, TNFalpha-induced caspase-8 activation contributes to DNA fragmentation but is not necessary for the loss of the inner mitochondrial transmembrane potential (DeltaPsim) or cell death. We here extend these observations to demonstrate that, when NF-kappaB is inhibited in macrophages, TNFalpha alters lysosomal membrane permeability (LMP). This results in the release of cathepsin B with subsequent loss of DeltaPsim and caspase-8 independent cell death. Interestingly, the cytoprotective, NF-kappaB-dependent protein A20 was rapidly induced in macrophages treated with TNFalpha. Ectopic expression of A20 in macrophages preserves LMP following treatment with TNFalpha, and as a result, mitochondrial integrity is safeguarded and macrophages are protected from cell death. These observations demonstrate that TNFalpha triggers both caspase 8-dependent and -independent cell death pathways in macrophages and identify a novel mechanism by which A20 protects these cells against both pathways.
Figures




Similar articles
-
NF-kappaB-regulated expression of cellular FLIP protects rheumatoid arthritis synovial fibroblasts from tumor necrosis factor alpha-mediated apoptosis.Arthritis Rheum. 2004 Dec;50(12):3844-55. doi: 10.1002/art.20680. Arthritis Rheum. 2004. PMID: 15593196
-
A20 promotes Brucella intracellular growth via inhibition of macrophage cell death and activation.Vet Microbiol. 2015 Jan 30;175(1):50-7. doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2014.11.006. Epub 2014 Nov 18. Vet Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 25433453
-
Interferon gamma (IFNgamma ) and tumor necrosis factor alpha synergism in ME-180 cervical cancer cell apoptosis and necrosis. IFNgamma inhibits cytoprotective NF-kappa B through STAT1/IRF-1 pathways.J Biol Chem. 2001 Apr 20;276(16):13153-9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M007646200. Epub 2001 Jan 18. J Biol Chem. 2001. PMID: 11278357
-
ABINs: A20 binding inhibitors of NF-kappa B and apoptosis signaling.Biochem Pharmacol. 2009 Jul 15;78(2):105-14. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2009.02.009. Epub 2009 Feb 27. Biochem Pharmacol. 2009. PMID: 19464428 Review.
-
Reactive oxygen species in TNFalpha-induced signaling and cell death.Mol Cells. 2010 Jul;30(1):1-12. doi: 10.1007/s10059-010-0105-0. Epub 2010 Jul 14. Mol Cells. 2010. PMID: 20652490 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Endolysosomal proteases and their inhibitors in immunity.Nat Rev Immunol. 2009 Dec;9(12):871-82. doi: 10.1038/nri2671. Nat Rev Immunol. 2009. PMID: 19935806 Review.
-
Effects of TNF receptor blockade on in vitro cell survival and response to negative energy balance in dairy cattle.J Anim Sci Biotechnol. 2018 Jan 10;9:6. doi: 10.1186/s40104-017-0224-y. eCollection 2018. J Anim Sci Biotechnol. 2018. PMID: 29344353 Free PMC article.
-
The deubiquitinase A20 mediates feedback inhibition of interleukin-17 receptor signaling.Sci Signal. 2013 Jun 4;6(278):ra44. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.2003699. Sci Signal. 2013. PMID: 23737552 Free PMC article.
-
Tumor necrosis factor-alpha-converting enzyme activities and tumor-associated macrophages in breast cancer.Immunol Res. 2014 Jan;58(1):87-100. doi: 10.1007/s12026-013-8434-7. Immunol Res. 2014. PMID: 24072428 Review.
-
Engineer a double team of short-lived and glucose-sensing bacteria for cancer eradication.Cell Rep Med. 2023 Jun 20;4(6):101043. doi: 10.1016/j.xcrm.2023.101043. Epub 2023 May 15. Cell Rep Med. 2023. PMID: 37192627 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Pope RM. Apoptosis as a therapeutic tool in rheumatoid arthritis. Nat Rev Immunol. 2002;2:527–35. - PubMed
-
- Sarzi-Puttini P, Atzeni F, Doria A, Iaccarino L, Turiel M. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha, biologic agents and cardiovascular risk. Lupus. 2005;14:780–4. - PubMed
-
- Tartaglia LA, Rothe M, Hu YF, Goeddel DV. Tumor necrosis factor’s cytotoxic activity is signaled by the p55 TNF receptor. Cell. 1993;73:213–6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

