The ribonome: a dominant force in co-ordinating gene expression
- PMID: 19152504
- PMCID: PMC4332539
- DOI: 10.1042/BC20080055
The ribonome: a dominant force in co-ordinating gene expression
Abstract
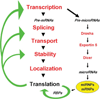
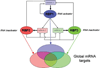
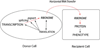
The ribonome is the total cellular complement of RNAs and their regulatory factors functioning dynamically in time and space within ribonucleoprotein complexes. We theorize that the ribonome is an ancient central co-ordinator that has evolved to communicate on multiple levels to the proteome on the one hand (feed-forward), and the transcriptome and RNA processing machinery on the other (feed-back). Furthermore, the ribonome can potentially communicate to other cells horizontally with implications for biological information transfer and for the evolution of both RNA and DNA operating systems. The post-transcriptional RNA operon theory of co-regulated gene expression accounts for the co-ordinated dynamics of RNA-binding proteins within the cellular ribonome, thus allowing for the recombination and remodelling of the RNPs (ribonucleoproteins) to generate new combinations of functionally related proteins. Thus, post-transcriptional RNA operons form the core of the ribonomic operating system in which both their control and co-ordination govern outcomes. Within the ribonome, RNA-binding proteins control one another's mRNAs to keep the global mRNA environment in balance. We argue that these post-transcriptional ribonomic systems provide an information management and distribution centre for evolutionary expansion of multicellularity in tissues, organs, organisms, and their communities.
Figures

References
-
- Aliotta JM, Sanchez-Guijo FM, Dooner GJ, Johnson KW, Dooner MS, Greer KA, Greer D, Pimentel J, Kolankiewicz LM, Puente N, et al. Alteration of marrow cell gene expression, protein production and engraftment into lung by lung-derived microvesicles: a novel mechanism for phenotype modulation. Stem Cells. 2007;25:2245–2256. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

