Cholera toxin inhibitors studied with high-performance liquid affinity chromatography: a robust method to evaluate receptor-ligand interactions
- PMID: 19152642
- PMCID: PMC2718734
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1747-0285.2008.00758.x
Cholera toxin inhibitors studied with high-performance liquid affinity chromatography: a robust method to evaluate receptor-ligand interactions
Abstract
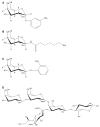
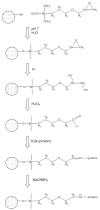
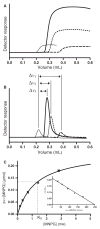
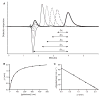
Anti-adhesion drugs may be an alternative to antibiotics to control infection of micro-organisms. The well-characterized interaction between cholera toxin and the cellular glycolipid GM1 makes it an attractive model for inhibition studies in general. In this report, we demonstrate a high-performance liquid affinity chromatography approach called weak affinity chromatography to evaluate cholera toxin inhibitors. The cholera toxin B-subunit was covalently coupled to porous silica and a (weak) affinity column was produced. The K(D) values of galactose and meta-nitrophenyl alpha-D-galactoside were determined with weak affinity chromatography to be 52 and 1 mM, respectively, which agree well with IC(50) values previously reported. To increase inhibition potency multivalent inhibitors have been developed and the interaction with multivalent glycopolypeptides was also evaluated. The affinity of these compounds was found to correlate with the galactoside content but K(D) values were not obtained because of the inhomogeneous response and slow off-rate from multivalent interactions. Despite the limitations in obtaining direct K(D) values of the multivalent galactopolypeptides, weak affinity chromatography represents an additional and valuable tool in the evaluation of monovalent as well as multivalent cholera toxin inhibitors. It offers multiple advantages, such as a low sample consumption, high reproducibility and short analysis time, which are often not observed in other methods of analysis.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Solution and crystallographic studies of branched multivalent ligands that inhibit the receptor-binding of cholera toxin.J Am Chem Soc. 2002 Nov 6;124(44):12991-8. doi: 10.1021/ja027584k. J Am Chem Soc. 2002. PMID: 12405825
-
Synthesis and cholera toxin binding properties of multivalent GM1 mimics.Org Biomol Chem. 2004 Jul 21;2(14):2113-24. doi: 10.1039/b405344c. Epub 2004 Jun 30. Org Biomol Chem. 2004. PMID: 15254640
-
Strong inhibition of cholera toxin by multivalent GM1 derivatives.Chembiochem. 2007 Sep 3;8(13):1500-3. doi: 10.1002/cbic.200700266. Chembiochem. 2007. PMID: 17625801 No abstract available.
-
Characterization and crystal structure of a high-affinity pentavalent receptor-binding inhibitor for cholera toxin and E. coli heat-labile enterotoxin.J Am Chem Soc. 2002 Jul 31;124(30):8818-24. doi: 10.1021/ja0202560. J Am Chem Soc. 2002. PMID: 12137534
-
Natural and synthetic cholera toxin antagonists.Mini Rev Med Chem. 2007 Feb;7(2):159-70. doi: 10.2174/138955707779802589. Mini Rev Med Chem. 2007. PMID: 17305590 Review.
Cited by
-
Pharmaceutical and biomedical applications of affinity chromatography: recent trends and developments.J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2012 Oct;69:93-105. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2012.01.004. Epub 2012 Jan 14. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2012. PMID: 22305083 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Imaging Saturation Transfer Difference (STD) NMR: Affinity and Specificity of Protein-Ligand Interactions from a Single NMR Sample.J Am Chem Soc. 2023 Aug 2;145(30):16391-16397. doi: 10.1021/jacs.3c02218. Epub 2023 Jul 24. J Am Chem Soc. 2023. PMID: 37487192 Free PMC article.
-
Probing the Origin of Affinity in the GM1-Cholera Toxin Complex through Site-Selective Editing with Fluorine.ACS Cent Sci. 2024 Jul 12;10(8):1481-1489. doi: 10.1021/acscentsci.4c00622. eCollection 2024 Aug 28. ACS Cent Sci. 2024. PMID: 39220706 Free PMC article.
-
Towards new cholera prophylactics and treatment: Crystal structures of bacterial enterotoxins in complex with GM1 mimics.Sci Rep. 2017 May 24;7(1):2326. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-02179-0. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28539625 Free PMC article.
-
Fragment screening of cyclin G-associated kinase by weak affinity chromatography.Anal Bioanal Chem. 2012 Nov;404(8):2417-25. doi: 10.1007/s00216-012-6335-6. Epub 2012 Aug 24. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2012. PMID: 22918538 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ofek I, Hasty DL, Sharon N. Anti-adhesion therapy of bacterial diseases: prospects and problems. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol. 2003;38:181–191. - PubMed
-
- Fan E, Merritt EA, Verlinde CL, Hol WG. AB(5) toxins: structures and inhibitor design. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2000;10:680–686. - PubMed
-
- Turnbull WB, Precious BL, Homans SW. Dissecting the cholera toxin-ganglioside GM1 interaction by isothermal titration calorimetry. J Am Chem Soc. 2004;126:1047–1054. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

