Quantitative intact specimen magnetic resonance microscopy at 3.0 T
- PMID: 19152774
- PMCID: PMC2708118
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mri.2008.11.008
Quantitative intact specimen magnetic resonance microscopy at 3.0 T
Abstract
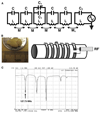
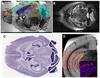
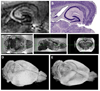
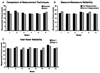
In this report, we discuss the application of a methodology for high-contrast, high-resolution magnetic resonance microscopy (MRM) of murine tissue using a 3.0-T imaging system. We employed a threefold strategy that included customized specimen preparation to maximize image contrast, three-dimensional data acquisition to minimize scan time and custom radiofrequency resonator design to maximize signal sensitivity. Images had a resolution of 100 x 78 x 78 microm(3) with a signal-to-noise ratio per voxel greater than 25:1 and excellent contrast-to-noise ratios over a 30-min acquisition. We quantitatively validated the methods through comparisons of neuroanatomy across two lines of genetically engineered mice. Specifically, we were able to detect volumetric differences of as little as 9% between genetically engineered mouse strains in multiple brain regions that were predictive of underlying impairments in brain development. The overall methodology was straightforward to implement and provides ready access to basic MRM at field strengths that are widely available in both the laboratory and the clinic.
Figures
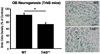
References
-
- Benveniste H, Blackband S. MR microscopy and high resolution small animal MRI: applications in neuroscience research. Prog Neurobiol. 2002;67:393–420. - PubMed
-
- Johnson GA, Cofer GP, Gewalt SL, Hedlund LW. Morphological phenotyping with MR microscopy: the visible mouse. Radiology. 2002;222:789–793. - PubMed
-
- Johnson GA, Thompson MB, Drayer BP, Bone SN. Magnetic resonance microscopy in neurologic models. Acta Radiol Suppl. 1986;369:267–268. - PubMed
-
- Johnson GA, Thompson MB, Gewalt SL, Hayes CE. Nuclear magnetic resonance imaging at microscopic resolution. J Magn Reson. 1986;68:129–137.
-
- Ballon DJ, Graham MC, Miodownik S, Koutcher JA. Doubly tuned solenoidal resonators for small animal imaging and spectroscopy at 1.5 tesla. Magn Reson Med. 1989;7:155–162. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

