Ultrafast fluorescence spectroscopy via upconversion applications to biophysics
- PMID: 19152860
- PMCID: PMC3439200
- DOI: 10.1016/S0076-6879(08)03408-3
Ultrafast fluorescence spectroscopy via upconversion applications to biophysics
Abstract
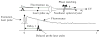
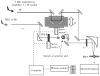
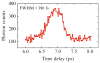
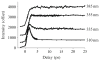
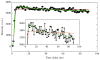
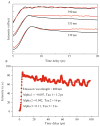
This chapter reviews basic concepts of nonlinear fluorescence upconversion, a technique whose temporal resolution is essentially limited only by the pulse width of the ultrafast laser. Design aspects for upconversion spectrophotofluorometers are discussed, and a recently developed system is described. We discuss applications in biophysics, particularly the measurement of time-resolved fluorescence spectra of proteins (with subpicosecond time resolution). Application of this technique to biophysical problems such as dynamics of tryptophan, peptides, proteins, and nucleic acids is reviewed.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Ultrafast Fluorescence Spectroscopy via Upconversion and Its Applications in Biophysics.Molecules. 2021 Jan 3;26(1):211. doi: 10.3390/molecules26010211. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 33401638 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Enhancement of protein spectra with tryptophan analogs: fluorescence spectroscopy of protein-protein and protein-nucleic acid interactions.Methods Enzymol. 1997;278:151-90. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(97)78010-8. Methods Enzymol. 1997. PMID: 9170313 Review. No abstract available.
-
Femtosecond studies of tryptophan fluorescence dynamics in proteins: local solvation and electronic quenching.J Phys Chem B. 2006 Sep 21;110(37):18097-103. doi: 10.1021/jp063025e. J Phys Chem B. 2006. PMID: 16970418
-
Ultrafast fluorescence dynamics of tryptophan in the proteins monellin and IIAGlc.J Am Chem Soc. 2006 Feb 1;128(4):1214-21. doi: 10.1021/ja055746h. J Am Chem Soc. 2006. PMID: 16433538
-
Laminar-flow fluid mixer for fast fluorescence kinetics studies.Biophys J. 2002 Nov;83(5):2872-8. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(02)75296-X. Biophys J. 2002. PMID: 12414719 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Pathlength-selective, interferometric diffuse correlation spectroscopy.IEEE J Sel Top Quantum Electron. 2025 Jul-Aug;31(4):7400814. doi: 10.1109/jstqe.2025.3575719. Epub 2025 Jun 2. IEEE J Sel Top Quantum Electron. 2025. PMID: 40766943
-
Quercetin•Zirconium Metal Complexes: Insights from Femto to Millisecond Photobehavior.Chemistry. 2025 Jun 23;31(35):e202500854. doi: 10.1002/chem.202500854. Epub 2025 May 22. Chemistry. 2025. PMID: 40354135 Free PMC article.
-
Fluorescence lifetime Hong-Ou-Mandel sensing.Nat Commun. 2023 Dec 4;14(1):8005. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-43868-x. Nat Commun. 2023. PMID: 38049423 Free PMC article.
-
The Way to Pursue Truly High-Performance Perovskite Solar Cells.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2019 Sep 5;9(9):1269. doi: 10.3390/nano9091269. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31492035 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ultrafast Fluorescence Spectroscopy via Upconversion and Its Applications in Biophysics.Molecules. 2021 Jan 3;26(1):211. doi: 10.3390/molecules26010211. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 33401638 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Andrews DL, Demidov AA. An introduction to laser spectroscopy. 2. Kluwer Academic/Plenum Publisher; New York: 2002.
-
- Arzhantsev S, Maroncelli M. Design and characterization of a femtosecond fluorescence spectrometer based on optical Kerr gating. Appl Spectrosc. 2005;59:206. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

