Acamprosate and naltrexone treatment effects on ethanol and sucrose seeking and intake in ethanol-dependent and nondependent rats
- PMID: 19153715
- PMCID: PMC2864152
- DOI: 10.1007/s00213-009-1465-z
Acamprosate and naltrexone treatment effects on ethanol and sucrose seeking and intake in ethanol-dependent and nondependent rats
Abstract
Rationale: Two pharmacotherapies are approved for treating alcohol craving (acamprosate and naltrexone), but both have shown mixed findings in animals and humans.
Objectives: The present experiments utilized a "reinforcer blocking" approach (i.e., rats were able to consume ethanol during treatment) to better understand the efficacy of these treatments for ethanol seeking and drinking using ethanol-dependent and nondependent rats.
Materials and methods: In "nondependent" experiments, drugs (acamprosate 50, 100, and 200 mg/kg; naltrexone 0.1, 0.3, and 1.0 mg/kg) were administered over 3-week periods prior to operant sessions with a low response requirement to gain access to reinforcers for 20 min. For "dependent" experiments, rats were made dependent in vapor/inhalation chambers.
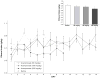
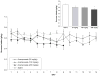
Results: Acamprosate and naltrexone had similar effects on intake in nondependent and dependent rats; neither drug was selective for ethanol over sucrose drinking. In nondependent animals, naltrexone was more efficacious at more doses than acamprosate, and acamprosate's effects were limited to a dose that also had adverse effects on body weight. Both pharmacotherapies showed more selectivity when examining reinforcer seeking. In nondependent rats, acamprosate and naltrexone had response-attenuating effects in ethanol, but not sucrose, groups. In dependent animals, acamprosate had selective effects limited to a decrease in sucrose seeking. Naltrexone, however, selectively decreased ethanol-seeking in nondependent rats.
Conclusions: The naltrexone-induced decreases in seeking suggested a change in incentive motivation which was selective for ethanol in nondependent rats. The "nondependent" paradigm may model early stages of "problem drinking" in humans, and the findings suggest that naltrexone could be a good intervention for this level of alcohol abuse and relapse prevention.
Figures



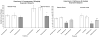
References
-
- Anton RF, O’Malley SS, Ciraulo DA, Cisler RA, Couper D, Donovan DM, Gastfriend DR, Hosking JD, Johnson BA, LoCastro JS, Longabaugh R, Mason BJ, Mattson ME, Miller WR, Pettinati HM, Randall CL, Swift R, Weiss RD, Williams LD, Zweben A COMBINE Study Research Group. Combined pharmacotherapies and behavioral interventions for alcohol dependence: the COMBINE Study: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA. 2006;295:2003–2017. - PubMed
-
- Anton RF, Oroszi G, O’Malley S, Couper D, Swift R, Pettinati H, Goldman D. An evaluation of mu-opioid receptor (OPRM1) as a predictor of naltrexone response in the treatment of alcohol dependence: results from the Combined Pharmacotherapies and Behavioral Interventions for Alcohol Dependence (COMBINE) Study. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2008;65:135–144. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bachteler D, Economidou D, Danysz W, Ciccocioppo R, Spanagel R. The effects of acamprosate and neramexane on cue-induced reinstatement of ethanol-seeking behavior in rat. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2005;30:1104–1110. - PubMed
-
- Baros AM, Latham PK, Moak DH, Voronin K, Anton RF. What role does measuring medication compliance play in evaluating the efficacy of naltrexone? Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2007;31:596–603. - PubMed
-
- Boismare F, Daoust M, Moore N, Saligaut C, Lhuintre JP, Chretien P, Durlach J. A homotaurine derivative reduces the voluntary intake of ethanol by rats: are cerebral GABA receptors involved? Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 1984;21:787–789. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

