RNA interference: from basic research to therapeutic applications
- PMID: 19153977
- PMCID: PMC7159607
- DOI: 10.1002/anie.200802092
RNA interference: from basic research to therapeutic applications
Abstract
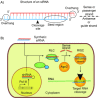
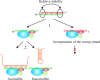
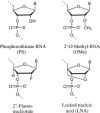
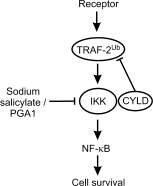
An efficient mechanism for the sequence-specific inhibition of gene expression is RNA interference. In this process, double-stranded RNA molecules induce cleavage of a selected target RNA (see picture). This technique has in recent years developed into a standard method of molecular biology. Successful applications in animal models have already led to the initiation of RNAi-based clinical trials as a new therapeutic option.Only ten years ago Andrew Fire and Craig Mello were able to show that double-stranded RNA molecules could inhibit the expression of homologous genes in eukaryotes. This process, termed RNA interference, has developed into a standard method of molecular biology. This Review provides an overview of the molecular processes involved, with a particular focus on the posttranscriptional inhibition of gene expression in mammalian cells, the possible applications in research, and the results of the first clinical studies.
Figures





Similar articles
-
RNA interference and potential therapeutic applications of short interfering RNAs.Cancer Gene Ther. 2005 Oct;12(10):787-95. doi: 10.1038/sj.cgt.7700857. Cancer Gene Ther. 2005. PMID: 15891770 Review.
-
RNA interference: big applause for silencing in Stockholm.Cell. 2006 Dec 15;127(6):1083-6. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2006.12.001. Cell. 2006. PMID: 17174883
-
RNAi therapeutics: principles, prospects and challenges.Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2007 Mar 30;59(2-3):75-86. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2007.03.005. Epub 2007 Mar 16. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2007. PMID: 17449137 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Update on the development of microRNA and siRNA molecules as regulators of cell physiology.Recent Pat DNA Gene Seq. 2010 Jun;4(2):113-21. doi: 10.2174/187221510793205755. Recent Pat DNA Gene Seq. 2010. PMID: 20550514 Review.
-
RNA interference and human disease.Mol Genet Metab. 2003 Sep-Oct;80(1-2):121-8. doi: 10.1016/j.ymgme.2003.08.011. Mol Genet Metab. 2003. PMID: 14567961 Review.
Cited by
-
The how and why of lncRNA function: An innate immune perspective.Biochim Biophys Acta Gene Regul Mech. 2020 Apr;1863(4):194419. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2019.194419. Epub 2019 Sep 2. Biochim Biophys Acta Gene Regul Mech. 2020. PMID: 31487549 Free PMC article. Review.
-
RNA interference-based functional knockdown of the voltage-gated potassium channel Kv7.2 in dorsal root ganglion neurons after in vitro and in vivo gene transfer by adeno-associated virus vectors.Mol Pain. 2018 Jan-Dec;14:1744806917749669. doi: 10.1177/1744806917749669. Epub 2017 Dec 6. Mol Pain. 2018. PMID: 29212407 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic potential of chemically modified siRNA: Recent trends.Chem Biol Drug Des. 2017 Nov;90(5):665-678. doi: 10.1111/cbdd.12993. Epub 2017 May 16. Chem Biol Drug Des. 2017. PMID: 28378934 Free PMC article. Review.
-
In vivo imaging of RNA interference.J Nucl Med. 2010 Feb;51(2):169-72. doi: 10.2967/jnumed.109.066878. Epub 2010 Jan 15. J Nucl Med. 2010. PMID: 20080892 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The chemistry and biology of oligonucleotide conjugates.Acc Chem Res. 2012 Jul 17;45(7):1067-76. doi: 10.1021/ar2002123. Epub 2012 Feb 21. Acc Chem Res. 2012. PMID: 22353142 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

