Microsatellite repeat instability and neurological disease
- PMID: 19154005
- PMCID: PMC4321794
- DOI: 10.1002/bies.080122
Microsatellite repeat instability and neurological disease
Abstract
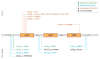
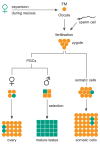
Over 20 unstable microsatellite repeats have been identified as the cause of neurological disease in humans. The repeat nucleotide sequences, their location within the genes, the ranges of normal and disease-causing repeat length and the clinical outcomes differ. Unstable repeats can be located in the coding or the non-coding region of a gene. Different pathogenic mechanisms that are hypothesised to underlie the diseases are discussed. Evidence is given both from studies in simple model systems and from studies on human material and in animal models. Since somatic instability might affect the clinical outcome, this is briefly touched on. Available data and theories on the timing and mechanisms of the repeat instability itself are discussed, along with factors that have been observed to affect instability. Finally, the question of why the often harmful unstable repeats have been maintained throughout evolution is addressed.
Figures

References
-
- Fu YH, Kuhl DP, Pizzuti A, Pieretti M, Sutcliffe JS, et al. Variation of the CGG repeat at the fragile X site results in genetic instability: resolution of the Sherman paradox. Cell. 1991;67:1047–1058. - PubMed
-
- La Spada AR, Wilson EM, Lubahn DB, Harding AE, Fischbeck KH. Androgen receptor gene mutations in X-linked spinal and bulbar muscular atrophy. Nature. 1991;352:77–79. - PubMed
-
- Richards RI, Sutherland GR. Heritable unstable DNA sequences. Nat Genet. 1992;1:7–9. - PubMed
-
- Orr HT, Zoghbi HY. Trinucleotide repeat disorders. Annu Rev Neurosci. 2007;30:575–621. - PubMed
-
- Mirkin SM. Expandable DNA repeats and human disease. Nature. 2007;447:932–940. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

