Inflammation mediates varying effects in neurogenesis: relevance to the pathogenesis of brain injury and neurodegenerative disorders
- PMID: 19154336
- PMCID: PMC2707502
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2009.05886.x
Inflammation mediates varying effects in neurogenesis: relevance to the pathogenesis of brain injury and neurodegenerative disorders
Abstract
Brain inflammation is a complex cellular and molecular response to stress, injury or infection of the CNS in attempt to defend against insults, clear dead and damaged neurons and return the CNS to a normal state. Inflammation in the CNS is driven by the activation of resident microglia, astrocytes and infiltrating peripheral macrophages, which release a plethora of anti- and pro-inflammatory cytokines, chemokines, neurotransmitters and reactive oxygen species. This inflammatory state inadvertently causes further bystander damage to neurons and produces both detrimental and favorable conditions for neurogenesis. Inflammatory factors have varying effects on neural progenitor cell proliferation, migration, differentiation, survival and incorporation of newly born neurons into the CNS circuitry. The unique profile of inflammatory factors, which depends on the severity of inflammation, can have varying consequences on neurogenesis. Inflammatory factors released during mild acute inflammation usually stimulate neurogenesis; where as the factors released by uncontrolled inflammation create an environment that is detrimental to neurogenesis. This review will provide a summary of current progress in this emerging field and examine the potential mechanisms through which inflammation affects neurogenesis during neurological complications.
Figures
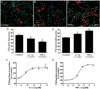
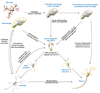
References
-
- Arvidsson A, Collin T, Kirik D, Kokaia Z, Lindvall O. Neuronal replacement from endogenous precursors in the adult brain after stroke. Nat Med. 2002;8:963–970. - PubMed
-
- Bai F, Bergeron M, Nelson DL. Chronic AMPA receptor potentiator (LY451646) treatment increases cell proliferation in adult rat hippocampus. Neuropharmacology. 2003;44:1013–1021. - PubMed
-
- Ben-Hur T, Ben-Menachem O, Furer V, Einstein O, Mizrachi-Kol R, Grigoriadis N. Effects of proinflammatory cytokines on the growth, fate, and motility of multipotential neural precursor cells. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2003;24:623–631. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

