Ablation of p120-catenin enhances invasion and metastasis of human lung cancer cells
- PMID: 19154401
- PMCID: PMC11158803
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2008.01067.x
Ablation of p120-catenin enhances invasion and metastasis of human lung cancer cells
Abstract
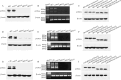
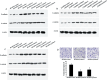
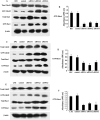
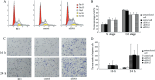
p120-catenin, a member of the Armadillo gene family, has emerged as both a master regulator of cadherin stability and an important modulator of small GTPase activities. Therefore, it plays novel roles in tumor malignant phenotype, such as invasion and metastasis. We have reported previously that abnormal expression of p120-catenin is associated with lymph node metastasis in lung squamous cell carcinomas (SCC) and adenocarcinomas. To investigate the role and possible mechanism of p120-catenin in lung cancer, we knocked down p120-catenin using small interfering RNA (siRNA). We found that ablation of p120-catenin reduced the levels of E-cadherin and beta-catenin proteins, as well as the mRNA of beta-catenin. Furthermore, p120-catenin depletion inactivated RhoA, but increased the activity of Cdc42 and Rac1, and promoted proliferation and the invasive ability of lung cancer cells both in vitro and in vivo. Our data reveal that p120-catenin gene knockdown enhances the metastasis of lung cancer cells, probably by either depressing cell-cell adhesion due to lower levels of E-cadherin and beta-catenin, or altering the activity of small GTPase, such as inactivation of RhoA and activation of Cdc42/Rac1.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Abnormal expression of p120-catenin, E-cadherin, and small GTPases is significantly associated with malignant phenotype of human lung cancer.Lung Cancer. 2009 Mar;63(3):375-82. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2008.12.012. Epub 2009 Jan 21. Lung Cancer. 2009. PMID: 19162367
-
Inhibition of RhoA by p120 catenin.Nat Cell Biol. 2000 Sep;2(9):637-44. doi: 10.1038/35023588. Nat Cell Biol. 2000. PMID: 10980705
-
p120 catenin is essential for mesenchymal cadherin-mediated regulation of cell motility and invasiveness.J Cell Biol. 2006 Sep 25;174(7):1087-96. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200605022. Epub 2006 Sep 18. J Cell Biol. 2006. PMID: 16982802 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging roles for p120-catenin in cell adhesion and cancer.Oncogene. 2004 Oct 18;23(48):7947-56. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1208161. Oncogene. 2004. PMID: 15489912 Review.
-
p120-catenin: Past and present.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2007 Jan;1773(1):2-7. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2006.09.019. Epub 2006 Sep 19. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2007. PMID: 17175391 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
P120-catenin isoforms 1 and 3 regulate proliferation and cell cycle of lung cancer cells via β-catenin and Kaiso respectively.PLoS One. 2012;7(1):e30303. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0030303. Epub 2012 Jan 20. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22276175 Free PMC article.
-
HER2/ErbB2-induced breast cancer cell migration and invasion require p120 catenin activation of Rac1 and Cdc42.J Biol Chem. 2010 Sep 17;285(38):29491-501. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.136770. Epub 2010 Jul 1. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20595387 Free PMC article.
-
Overexpression of PTPRZ1 Regulates p120/β-Catenin Phosphorylation to Promote Carcinogenesis of Oral Submucous Fibrosis.J Oncol. 2022 Feb 23;2022:2352360. doi: 10.1155/2022/2352360. eCollection 2022. J Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35251170 Free PMC article.
-
p120-catenin down-regulation and epidermal growth factor receptor overexpression results in a transformed epithelium that mimics esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.Am J Pathol. 2015 Jan;185(1):240-51. doi: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2014.09.008. Am J Pathol. 2015. PMID: 25529795 Free PMC article.
-
p120 catenin: an essential regulator of cadherin stability, adhesion-induced signaling, and cancer progression.Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci. 2013;116:409-32. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-394311-8.00018-2. Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci. 2013. PMID: 23481205 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bremnes RM, Veve R, Gabrielson E et al . High‐throughput tissue microarray analysis used to evaluate biology and prognostic significance of the E‐cadherin pathway in non‐small‐cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol 2002; 20: 2417–28. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

