Epidermal growth factor receptor lacking C-terminal autophosphorylation sites retains signal transduction and high sensitivity to epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor
- PMID: 19154417
- PMCID: PMC11158727
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2008.01071.x
Epidermal growth factor receptor lacking C-terminal autophosphorylation sites retains signal transduction and high sensitivity to epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor
Abstract
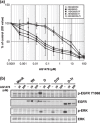
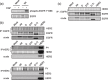
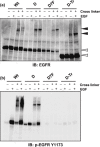
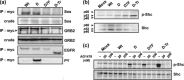
Constitutively active mutations of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) (delE746_A750) activate downstream signals, such as ERK and Akt, through the phosphorylation of tyrosine residues in the C-terminal region of EGFR. These pathways are thought to be important for cellular sensitivity to EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKI). To examine the correlation between phosphorylation of the tyrosine residues in the C-terminal region of EGFR and cellular sensitivity to EGFR TKI, we used wild-type (wt) EGFR, as well as the following constructs: delE746_A750 EGFR; delE746_A750 EGFR with substitution of seven tyrosine residues to phenylalanine in the C-terminal region; and delE746_A750 EGFR with a C-terminal truncation at amino acid 980. These constructs were transfected stably into HEK293 cells and designated HEK293/Wt, HEK293/D, HEK293/D7F, and HEK293/D-Tr, respectively. The HEK293/D cells were found to be 100-fold more sensitive to EGFR TKI (AG1478) than HEK293/Wt. Surprisingly, the HEK293/D7F and HEK293/D-Tr cells, transfected with EGFR lacking the C-terminal autophosphorylation sites, retained high sensitivity to EGFR TKI. In these three high-sensitivity cells, the ERK pathway was activated without ligand stimulation, which was inhibited by EGFR TKI. In addition, although EGFR in the HEK293/D7F and HEK293/D-Tr cells lacked significant tyrosine residues for EGFR signal transduction, phosphorylation of Src homology and collagen homology (Shc) was spontaneously activated in these cells. Our results indicate that tyrosine residues in the C-terminal region of EGFR are not required for cellular sensitivity to EGFR TKI, and that an as-yet-unknown signaling pathway of EGFR may exist that is independent of the C-terminal region of EGFR.
Figures


Similar articles
-
c-Jun N-terminal kinase activation by hydrogen peroxide in endothelial cells involves SRC-dependent epidermal growth factor receptor transactivation.J Biol Chem. 2001 May 11;276(19):16045-50. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M011766200. Epub 2001 Feb 27. J Biol Chem. 2001. PMID: 11278982
-
Cross-talk between the receptor tyrosine kinases Ron and epidermal growth factor receptor.Exp Cell Res. 2003 Oct 1;289(2):317-25. doi: 10.1016/s0014-4827(03)00280-5. Exp Cell Res. 2003. PMID: 14499632
-
Cholesterol depletion from the plasma membrane triggers ligand-independent activation of the epidermal growth factor receptor.J Biol Chem. 2002 Dec 20;277(51):49631-7. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M208327200. Epub 2002 Oct 22. J Biol Chem. 2002. PMID: 12397069
-
Mutational activation of ErbB family receptor tyrosine kinases: insights into mechanisms of signal transduction and tumorigenesis.Bioessays. 2007 Jun;29(6):558-65. doi: 10.1002/bies.20582. Bioessays. 2007. PMID: 17508401 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The ErbB kinase domain: structural perspectives into kinase activation and inhibition.Exp Cell Res. 2009 Feb 15;315(4):649-58. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2008.07.031. Epub 2008 Aug 15. Exp Cell Res. 2009. PMID: 18761339 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Bispecific designed ankyrin repeat proteins (DARPins) targeting epidermal growth factor receptor inhibit A431 cell proliferation and receptor recycling.J Biol Chem. 2011 Dec 2;286(48):41273-41285. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.293266. Epub 2011 Oct 6. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21979953 Free PMC article.
-
Potential roles of Centipede Scolopendra extracts as a strategy against EGFR-dependent cancers.Am J Transl Res. 2015 Jan 15;7(1):39-52. eCollection 2015. Am J Transl Res. 2015. PMID: 25755827 Free PMC article.
-
Impaired degradation followed by enhanced recycling of epidermal growth factor receptor caused by hypo-phosphorylation of tyrosine 1045 in RBE cells.BMC Cancer. 2012 May 16;12:179. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-12-179. BMC Cancer. 2012. PMID: 22591401 Free PMC article.
-
Sensitivities to various epidermal growth factor receptor-tyrosine kinase inhibitors of uncommon epidermal growth factor receptor mutations L861Q and S768I: What is the optimal epidermal growth factor receptor-tyrosine kinase inhibitor?Cancer Sci. 2016 Aug;107(8):1134-40. doi: 10.1111/cas.12980. Epub 2016 Jul 14. Cancer Sci. 2016. PMID: 27240419 Free PMC article.
-
Cetuximab response of lung cancer-derived EGF receptor mutants is associated with asymmetric dimerization.Cancer Res. 2013 Nov 15;73(22):6770-9. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-13-1145. Epub 2013 Sep 24. Cancer Res. 2013. PMID: 24063894 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gusterson B, Cowley G, McIlhinney J, Ozanne B, Fisher C, Reeves B. Evidence for increased epidermal growth factor receptors in human sarcomas. Int J Cancer 1985; 36: 689–93. - PubMed
-
- Bargmann CI, Hung MC, Weinberg RA. The neu oncogene encodes an epidermal growth factor receptor‐related protein. Nature 1986; 319: 226–30. - PubMed
-
- Mendelsohn J, Baselga J. Epidermal growth factor receptor targeting in cancer. Semin Oncol 2006; 33: 369–85. - PubMed
-
- Karamouzis MV, Grandis JR, Argiris A. Therapies directed against epidermal growth factor receptor in aerodigestive carcinomas. JAMA 2007; 298: 70–82. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

