Tachykinin receptor modulation of cyclooxygenase-2 expression in human polymorphonuclear leucocytes
- PMID: 19154444
- PMCID: PMC2697683
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2008.00033.x
Tachykinin receptor modulation of cyclooxygenase-2 expression in human polymorphonuclear leucocytes
Abstract
Background and purpose: We investigated the ability of natural and synthetic selective NK receptors agonists and antagonists to modulate cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) expression in human polymorphonuclear leucocytes (PMNs).
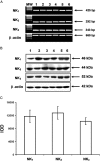
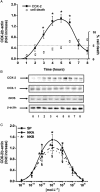
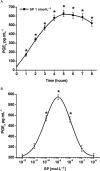
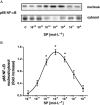
Experimental approach: The presence of all three tachykinin in PMNs was assessed by Western blot and PCR techniques. Natural and synthetic ligands selective for the tachykinin receptors were used to modulate COX-2 protein (measured with Western blotting) and activity [as prostaglandin E(2) (PGE(2)) output]. Effects of substance P (SP) on phosphorylation of mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs) and nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-kappaB) activation were studied to analyse the signalling pathway involved in COX-2 up-regulation mediated by SP.
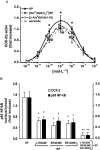
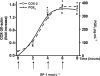
Key results: Stimulation of NK receptors with the natural ligands SP, neurokinin A (NKA) and neurokinin B, in the pmol.L(-1)-micromol.L(-1) concentration range, modulated COX-2 expression and PGE(2) release in a concentration- and time-dependent manner. Experiments with synthetic selective agonists [Sar(9), Met(O(2))(11)]SP, [beta-Ala(8)] NKA(4-10), senktide or selective antagonists L703,606, SR48,968 or SR142801, confirmed that COX-2 up-regulation was mediated by NK receptors. We found that mainly p38, p42 and p46 MAPKs were phosphorylated by SP and SB202190, PD98059 and SP600125, which are selective inhibitors of these kinases, blocked SP-induced COX-2 expression. SP also induced nuclear translocation of NF-kappaB concentration-dependently, with a maximum effect at 1 nmol.L(-1).
Conclusions and implications: Human PMNs possess functional NK(1), NK(2) and NK(3) receptors, which mediate the induction of COX-2 expression and NF-kappaB activation by SP.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Substance P-induced cyclooxygenase-2 expression in human umbilical vein endothelial cells.Br J Pharmacol. 2006 Mar;147(6):681-9. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0706660. Br J Pharmacol. 2006. PMID: 16432508 Free PMC article.
-
Respiratory actions of tachykinins in the nucleus of the solitary tract: characterization of receptors using selective agonists and antagonists.Br J Pharmacol. 2000 Mar;129(6):1121-31. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0703172. Br J Pharmacol. 2000. PMID: 10725260 Free PMC article.
-
Induction of cyclooxygenase-2 expression in human tracheal smooth muscle cells by interleukin-1beta: involvement of p42/p44 and p38 mitogen-activated protein kinases and nuclear factor-kappaB.J Biomed Sci. 2004 May-Jun;11(3):377-90. doi: 10.1007/BF02254443. J Biomed Sci. 2004. PMID: 15067222
-
PAR1-dependent COX-2/PGE2 production contributes to cell proliferation via EP2 receptors in primary human cardiomyocytes.Br J Pharmacol. 2014 Oct;171(19):4504-19. doi: 10.1111/bph.12794. Epub 2014 Sep 5. Br J Pharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24902855 Free PMC article.
-
Role of nitric oxide and septide-insensitive NK(1) receptors in bronchoconstriction induced by aerosolised neurokinin A in guinea-pigs.Br J Pharmacol. 2000 Mar;129(5):915-20. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0703135. Br J Pharmacol. 2000. PMID: 10696090 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Innate immune properties of selected human neuropeptides against Moraxella catarrhalis and nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae.BMC Immunol. 2012 May 2;13:24. doi: 10.1186/1471-2172-13-24. BMC Immunol. 2012. PMID: 22551165 Free PMC article.
-
TRPV1 and SP: key elements for sepsis outcome?Br J Pharmacol. 2013 Dec;170(7):1279-92. doi: 10.1111/bph.12056. Br J Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23145480 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cardiocirculatory pathophysiological mechanisms in severe acute pancreatitis.World J Gastrointest Pharmacol Ther. 2010 Feb 6;1(1):9-14. doi: 10.4292/wjgpt.v1.i1.9. World J Gastrointest Pharmacol Ther. 2010. PMID: 21577289 Free PMC article.
-
Direct and indirect antimicrobial activities of neuropeptides and their therapeutic potential.Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2012 Dec;13(8):723-38. doi: 10.2174/138920312804871139. Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2012. PMID: 23305360 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Annexin A1 N-terminal derived Peptide ac2-26 exerts chemokinetic effects on human neutrophils.Front Pharmacol. 2012 Feb 28;3:28. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2012.00028. eCollection 2012. Front Pharmacol. 2012. PMID: 22403546 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Azzolina A, Guarneri P, Lampisi N. Involvement of p38 and JNK MAPKs pathways in substance P-induced production of TNF-alpha by peritoneal mast cells. Cytokine. 2002;18:72–80. - PubMed
-
- Baldwin AS., Jr The NF-kappa B and I kappa B proteins: new discoveries and insights. Annu Rev Immunol. 1996;14:649–683. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

