Effects of ageing and streptozotocin-induced diabetes on connexin43 and P2 purinoceptor expression in the rat corpora cavernosa and urinary bladder
- PMID: 19154470
- PMCID: PMC3422638
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1464-410X.2008.08337.x
Effects of ageing and streptozotocin-induced diabetes on connexin43 and P2 purinoceptor expression in the rat corpora cavernosa and urinary bladder
Abstract
Objective: To investigate whether ageing and diabetes alter the expression of the gap junction protein connexin43 (Cx43) and of particular purinoceptor (P2R) subtypes in the corpus cavernosum and urinary bladder, and determine whether changes in expression of these proteins correlate with development of erectile and bladder dysfunction in diabetic and ageing rats.
Materials and methods: Erectile and bladder function of streptozotocin (STZ)-induced diabetic, insulin-treated and age-matched control Fischer-344 rats were evaluated 2, 4 and 8 months after diabetes induction by in vivo cystometry and cavernosometry. Corporal and bladder tissue were then isolated at each of these sample times and protein expression levels of Cx43 and of various P2R subtypes were determined by Western blotting.
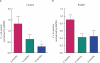
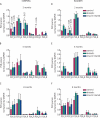
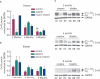
Results: In the corpora of control rats ageing was accompanied by a significant decrease in Cx43 and P2X(1)R, and increase in P2X(7)R expression. There was decreased Cx43 and increased P2Y(4)R expression in the ageing control rat bladder. There was a significant negative correlation between erectile capacity and P2X(1)R expression levels, and a positive correlation between bladder spontaneous activity and P2Y(4)R expression levels. There was already development of erectile dysfunction and bladder overactivity at 2 months after inducing diabetes, the earliest sample measured in the study. The development of these urogenital complications was accompanied by significant decreases in Cx43, P2Y(2)R, P2X(4)R and increase in P2X(1)R expression in the corpora, and by a doubling in Cx43 and P2Y(2)R, and significant increase in P2Y(4)R expression in the bladder. Changes in Cx43 and P2R expression were largely prevented by insulin therapy.
Conclusion: Ageing and diabetes mellitus markedly altered the expression of the gap junction protein Cx43 and of particular P2R subtypes in the rat penile corpora and urinary bladder. These changes in Cx43 and P2R expression provide the molecular substrate for altered gap junction and purinergic signalling in these tissues, and thus probably contribute to the early development of erectile dysfunction and higher detrusor activity in ageing and in diabetic rats.
Figures
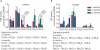
Similar articles
-
Longitudinal studies of time-dependent changes in both bladder and erectile function after streptozotocin-induced diabetes in Fischer 344 male rats.BJU Int. 2009 Nov;104(9):1292-300. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-410X.2009.08573.x. Epub 2009 Apr 15. BJU Int. 2009. PMID: 19389003
-
Effects of streptozotocin-induced diabetes on bladder and erectile (dys)function in the same rat in vivo.BJU Int. 2006 May;97(5):1076-82. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-410X.2006.06058.x. BJU Int. 2006. PMID: 16643495
-
Penile alterations at early stage of type 1 diabetes in rats.Int Braz J Urol. 2017 Jul-Aug;43(4):753-761. doi: 10.1590/S1677-5538.IBJU.2016.0454. Int Braz J Urol. 2017. PMID: 28338308 Free PMC article.
-
Alterations of connexin 43 in the diabetic rat heart.Adv Cardiol. 2006;42:243-254. doi: 10.1159/000092573. Adv Cardiol. 2006. PMID: 16646595 Review.
-
Purinergic signalling during development and ageing.Purinergic Signal. 2015 Sep;11(3):277-305. doi: 10.1007/s11302-015-9452-9. Epub 2015 May 20. Purinergic Signal. 2015. PMID: 25989750 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Connexins and diabetes.Cardiol Res Pract. 2012;2012:496904. doi: 10.1155/2012/496904. Epub 2012 Mar 1. Cardiol Res Pract. 2012. PMID: 22536530 Free PMC article.
-
Research Findings on Overactive Bladder.Curr Urol. 2015 May;8(1):1-21. doi: 10.1159/000365682. Epub 2015 May 20. Curr Urol. 2015. PMID: 26195957 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Involvement of urinary bladder Connexin43 and the circadian clock in coordination of diurnal micturition rhythm.Nat Commun. 2012 May 1;3:809. doi: 10.1038/ncomms1812. Nat Commun. 2012. PMID: 22549838 Free PMC article.
-
Purinergic signalling in the urinary tract in health and disease.Purinergic Signal. 2014 Mar;10(1):103-55. doi: 10.1007/s11302-013-9395-y. Epub 2013 Nov 22. Purinergic Signal. 2014. PMID: 24265069 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pannexin 1 channels play essential roles in urothelial mechanotransduction and intercellular signaling.PLoS One. 2014 Aug 29;9(8):e106269. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0106269. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25170954 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Campos de Carvalho AC, Roy C, Moreno AP, et al. Gap junctions formed of connexin43 are found between smooth muscle cells of human corpus cavernosum. J Urol. 1993;149:1568–75. - PubMed
-
- Neuhaus J, Weimann A, Stolzenburg JU, Wolburg H, Horn LC, Dorschner W. Smooth muscle cells from human urinary bladder express connexin43 in vivo and in vitro. World J Urol. 2002;20:250–4. - PubMed
-
- Christ GJ, Richards S, Winkler A. Integrative erectile biology: the role of signal transduction and cell-to-cell communication in coordinating corporal smooth muscle tone and penile erection. Int J Impot Res. 1997;9:69–84. - PubMed
-
- Brink PR, Valiunas V, Wang HZ, Zhao W, Davies K, Christ GJ. Experimental diabetes alters connexin43 derived gap junction permeability in short-term cultures of rat corporeal vascular smooth muscle cells. J Urol. 2006;175:381–6. - PubMed
-
- Serels S, Day NS, Wen YP, et al. Molecular studies of human connexin43 (Cx43) expression in isolated corporal tissue strips and cultured corporal smooth muscle cells. Int J Impot Res. 1998;10:135–43. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

