RP105 facilitates macrophage activation by Mycobacterium tuberculosis lipoproteins
- PMID: 19154986
- PMCID: PMC2742161
- DOI: 10.1016/j.chom.2008.12.002
RP105 facilitates macrophage activation by Mycobacterium tuberculosis lipoproteins
Abstract
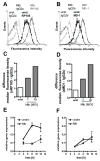
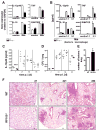
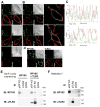
RP105, phylogenetically related to Toll-like receptor (TLR)-4, is reported to facilitate B cell activation by the TLR4-agonist lipopolysaccharide (LPS)--but to limit LPS-induced cytokine production by antigen-presenting cells. Here, we show that the role of RP105 extends beyond LPS recognition and that RP105 positively regulates macrophage responses to Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Mtb) lipoproteins. Mtb-infected RP105(-/-) mice exhibited impaired proinflammatory cytokine responses associated with enhanced bacterial burden and increased lung pathology. The Mtb 19 kDa lipoprotein induced release of tumor necrosis factor in a manner dependent on both TLR2 and RP105, and macrophage activation by Mtb lacking mature lipoproteins was not RP105 dependent. Thus, mycobacterial lipoproteins are RP105 agonists. RP105 physically interacted with TLR2, and both RP105 and TLR2 were required for optimal macrophage activation by Mtb. Our data identify RP105 as an accessory molecule for TLR2, forming part of the receptor complex for innate immune recognition of mycobacterial lipoproteins.
Figures

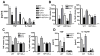
Similar articles
-
The N-terminal peptide moiety of the Mycobacterium tuberculosis 19 kDa lipoprotein harbors RP105-agonistic properties.J Leukoc Biol. 2018 Feb;103(2):311-319. doi: 10.1002/JLB.2MA0517-190RR. Epub 2018 Jan 9. J Leukoc Biol. 2018. PMID: 29345364
-
RP105 involved in activation of mouse macrophages via TLR2 and TLR4 signaling.Mol Cell Biochem. 2013 Jun;378(1-2):183-93. doi: 10.1007/s11010-013-1609-7. Epub 2013 Mar 13. Mol Cell Biochem. 2013. PMID: 23483427
-
Distinct contributions of the innate immune receptors TLR2 and RP105 to formation and architecture of structured lung granulomas in mice infected with Mycobacterium tuberculosis.Immunology. 2023 May;169(1):13-26. doi: 10.1111/imm.13606. Epub 2022 Nov 22. Immunology. 2023. PMID: 36370035
-
Toll-like receptor 2 in host defense against Mycobacterium tuberculosis: to be or not to be-that is the question.Curr Opin Immunol. 2016 Oct;42:76-82. doi: 10.1016/j.coi.2016.06.003. Epub 2016 Jun 18. Curr Opin Immunol. 2016. PMID: 27326654 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of toll-like receptor 2 in survival strategies of Mycobacterium tuberculosis in macrophage phagosomes.Anticancer Res. 2009 Mar;29(3):907-10. Anticancer Res. 2009. PMID: 19414326 Review.
Cited by
-
The Role of TLR2 in Infection and Immunity.Front Immunol. 2012 Apr 18;3:79. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2012.00079. eCollection 2012. Front Immunol. 2012. PMID: 22566960 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms of lung damage in tuberculosis: implications for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2023 Jun 21;13:1146571. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2023.1146571. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37415827 Free PMC article. Review.
-
M. tuberculosis induces potent activation of IDO-1, but this is not essential for the immunological control of infection.PLoS One. 2012;7(5):e37314. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0037314. Epub 2012 May 23. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22649518 Free PMC article.
-
Mycobacterium tuberculosis-macrophage interaction: Molecular updates.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2023 Mar 3;13:1062963. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2023.1062963. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 36936766 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Underwhelming or Misunderstood? Genetic Variability of Pattern Recognition Receptors in Immune Responses and Resistance to Mycobacterium tuberculosis.Front Immunol. 2021 Jun 30;12:714808. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.714808. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34276708 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Banaiee N, Kincaid EZ, Buchwald U, Jacobs WR, Jr, Ernst JD. Potent inhibition of macrophage responses to IFN-gamma by live virulent Mycobacterium tuberculosis is independent of mature mycobacterial lipoproteins but dependent on TLR2. J Immunol. 2006;176:3019–3027. - PubMed
-
- Black RA, Rauch CT, Kozlosky CJ, Peschon JJ, Slack JL, Wolfson MF, Castner BJ, Stocking KL, Reddy P, Srinivasan S, et al. A metalloproteinase disintegrin that releases tumour-necrosis factor-alpha from cells. Nature. 1997;385:729–733. - PubMed
-
- Blumenthal A, Lauber J, Hoffmann R, Ernst M, Keller C, Buer J, Ehlers S, Reiling N. Common and unique gene expression signatures of human macrophages in response to four strains of Mycobacterium avium that differ in their growth and persistence characteristics. Infect Immun. 2005;73:3330–3341. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

