Surfactant protein A modulates cell surface expression of CR3 on alveolar macrophages and enhances CR3-mediated phagocytosis
- PMID: 19155216
- PMCID: PMC2658045
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M808643200
Surfactant protein A modulates cell surface expression of CR3 on alveolar macrophages and enhances CR3-mediated phagocytosis
Abstract
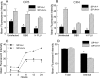
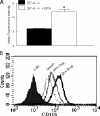
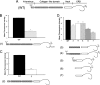
Pulmonary surfactant protein A (SP-A), a member of the collectin family, plays an important role in innate immune defense of the lung. In this study, we examined the role of SP-A in modulating complement receptor-mediated phagocytosis. Complement receptors (CR), CR3 (CD11b), and CR4 (CD11c) were expressed at reduced levels on the surface of alveolar macrophages from Sp-a(-/-) compared with Sp-a(+/+) mice. Administration of intratracheal SP-A to Sp-a(-/-) mice induced the translocation of CR3 from alveolar macrophage intracellular pools to the cell surface. Intratracheal challenge with Haemophilus influenza enhanced CR3 expression on the surface of alveolar macrophages from Sp-a(-/-) and Sp-a(+/+) mice, but relative expression remained lower in the Sp-a(-/-) mice at all time points post-inoculation. The effects of SP-A on macrophage and neutrophil CR3 redistribution between intracellular and cell surface pools were restricted to cells isolated from the lung. SP-A augmented CR3-mediated phagocytosis in a manner that was attenuated by N-glycanase or collagenase treatment of SP-A, implicating the N-linked sugar and collagen-like domains in that function. The binding of CR3 to SP-A was calcium dependent and mediated by the I-domain of CR3 and to a lesser extent by the CR3 lectin domain. Mapping of the domains of SP-A that were required for optimal binding to CR3 revealed that the N-linked sugars were more critical than the collagen-like domain or the extent of oligomeric assembly. We conclude that SP-A modulates the cell surface expression of CR3 on alveolar macrophages, binds to CR3, and enhances CR3-mediated phagocytosis.
Figures


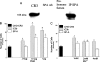
Similar articles
-
The role of CR3 (CD11b/CD18) and CR4 (CD11c/CD18) in complement-mediated phagocytosis and podosome formation by human phagocytes.Immunol Lett. 2017 Sep;189:64-72. doi: 10.1016/j.imlet.2017.05.014. Epub 2017 May 26. Immunol Lett. 2017. PMID: 28554712
-
Pulmonary surfactant protein A up-regulates activity of the mannose receptor, a pattern recognition receptor expressed on human macrophages.J Immunol. 2002 Oct 1;169(7):3565-73. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.169.7.3565. J Immunol. 2002. PMID: 12244146
-
CR3 (CD11b/CD18) and CR4 (CD11c/CD18) are involved in complement-independent antibody-mediated phagocytosis of Cryptococcus neoformans.Immunity. 2002 Jun;16(6):791-802. doi: 10.1016/s1074-7613(02)00328-x. Immunity. 2002. PMID: 12121661
-
Immunoregulatory function of SP-A.Mol Immunol. 2024 Feb;166:58-64. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2024.01.005. Epub 2024 Jan 19. Mol Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38244369 Review.
-
Structural Immunology of Complement Receptors 3 and 4.Front Immunol. 2018 Nov 26;9:2716. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.02716. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 30534123 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
SP-R210 (Myo18A) Isoforms as Intrinsic Modulators of Macrophage Priming and Activation.PLoS One. 2015 May 12;10(5):e0126576. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0126576. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25965346 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of Virulence Factors of Staphylococcus aureus: Novel Function of Known Virulence Factors That Are Implicated in Activation of Airway Epithelial Proinflammatory Response.J Pathog. 2011;2011:601905. doi: 10.4061/2011/601905. Epub 2011 Sep 14. J Pathog. 2011. PMID: 22567334 Free PMC article.
-
The Lung Alveolar Cell (LAC) miRNome and Gene Expression Profile of the SP-A-KO Mice After Infection With and Without Rescue With Human Surfactant Protein-A2 (1A0).Front Immunol. 2022 Jul 1;13:854434. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.854434. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35844510 Free PMC article.
-
C-type lectins with a sweet spot for Mycobacterium tuberculosis.Eur J Microbiol Immunol (Bp). 2011 Mar;1(1):25-40. doi: 10.1556/EuJMI.1.2011.1.6. Eur J Microbiol Immunol (Bp). 2011. PMID: 24466434 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Surfactant protein A (SP-A)-mediated clearance of Staphylococcus aureus involves binding of SP-A to the staphylococcal adhesin eap and the macrophage receptors SP-A receptor 210 and scavenger receptor class A.J Biol Chem. 2011 Feb 11;286(6):4854-70. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.125567. Epub 2010 Dec 1. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21123169 Free PMC article.
References
-
- LeVine, A. M., and Whitsett, J. A. (2001) Microbes Infect. 3 161–166 - PubMed
-
- Korfhagen, T. R. (2001) Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 25 668–672 - PubMed
-
- Khoor, A., Gray, M. E., Hull, W. M., Whitsett, J. A., and Stahlman, M. T. (1993) J. Histochem. Cytochem. 41 1311–1319 - PubMed
-
- Manz-Keinke, H., Plattner, H., and Schlepper-Schafer, J. (1992) Eur. J. Cell Biol. 57 95–100 - PubMed
-
- Ohmer-Schrock, D., Schlatterer, C., Plattner, H., and Schlepper-Schafer, J. (1995) J. Cell Sci. 108, 3695–3702 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

