Specific recognition of a multiply phosphorylated motif in the DNA repair scaffold XRCC1 by the FHA domain of human PNK
- PMID: 19155274
- PMCID: PMC2655680
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkn1086
Specific recognition of a multiply phosphorylated motif in the DNA repair scaffold XRCC1 by the FHA domain of human PNK
Abstract
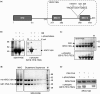
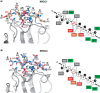
Short-patch repair of DNA single-strand breaks and gaps (SSB) is coordinated by XRCC1, a scaffold protein that recruits the DNA polymerase and DNA ligase required for filling and sealing the damaged strand. XRCC1 can also recruit end-processing enzymes, such as PNK (polynucleotide kinase 3'-phosphatase), Aprataxin and APLF (aprataxin/PNK-like factor), which ensure the availability of a free 3'-hydroxyl on one side of the gap, and a 5'-phosphate group on the other, for the polymerase and ligase reactions respectively. PNK binds to a phosphorylated segment of XRCC1 (between its two C-terminal BRCT domains) via its Forkhead-associated (FHA) domain. We show here, contrary to previous studies, that the FHA domain of PNK binds specifically, and with high affinity to a multiply phosphorylated motif in XRCC1 containing a pSer-pThr dipeptide, and forms a 2:1 PNK:XRCC1 complex. The high-resolution crystal structure of a PNK-FHA-XRCC1 phosphopeptide complex reveals the basis for this unusual bis-phosphopeptide recognition, which is probably a common feature of the known XRCC1-associating end-processing enzymes.
Figures


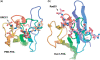

References
-
- Cappelli E, Taylor R, Cevasco M, Abbondandolo A, Caldecott K, Frosina G. Involvement of XRCC1 and DNA ligase III gene products in DNA base excision repair. J. Biol. Chem. 1997;272:23970–23975. - PubMed
-
- Rass U, Ahel I, West SC. Defective DNA repair and neurodegenerative disease. Cell. 2007;130:991–1004. - PubMed
-
- Jilani A, Ramotar D, Slack C, Ong C, Yang XM, Scherer SW, Lasko DD. Molecular cloning of the human gene, PNKP, encoding a polynucleotide kinase 3'-phosphatase and evidence for its role in repair of DNA strand breaks caused by oxidative damage. J. Biol. Chem. 1999;274:24176–24186. - PubMed
-
- Mani RS, Karimi-Busheri F, Cass CE, Weinfeld M. Physical properties of human polynucleotide kinase: hydrodynamic and spectroscopic studies. Biochemistry. 2001;40:12967–12973. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

