Role of radiology in geriatric care: a primer for family physicians
- PMID: 19155363
- PMCID: PMC2628843
Role of radiology in geriatric care: a primer for family physicians
Abstract
Objective: To present family physicians with the options available for diagnosing and treating a selection of common diseases in the elderly using diagnostic and interventional radiology.
Quality of evidence: Articles providing level I or II evidence were included in our review. Most articles presented results from randomized or other case-controlled studies.
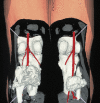
Main message: Geriatric care has become a complicated, multidisciplinary effort, with the family physician often leading the team. The expanding cohort of patients is not only better informed than their predecessors, but also more demanding of better care through cutting-edge technology and treatment. Specifically, the role of radiology has expanded quickly in geriatric medicine. Because of complex clinical presentations and rising costs, it is essential for primary care physicians to understand the appropriate use of imaging and radiological intervention.
Conclusion: There are a number of new and innovative radiological techniques and procedures available for elderly patients. This review aims to inform primary care physicians of a selected number of these techniques.
OBJECTIF: Présenter aux médecins de famille les options disponibles pour diagnostiquer et traiter un certain nombre de maladies fréquentes chez les personnes âgées à l’aide de la radiologie diagnostique et d’intervention.
QUALITÉ DES PREUVES: Notre revue comporte des articles contenant des preuves de niveau I ou II. Dans la plupart des articles, les résultats provenaient d’essais cliniques randomisés ou d’études cas-témoin.
PRINCIPAL MESSAGE: Les soins gériatriques exigent maintenant des interventions complexes d’une équipe multidisciplinaires dont le médecin de famille est souvent le chef. La cohorte grandissante de ces patients est non seulement mieux informée que les précédentes, mais elle exige aussi de meilleurs soins basés sur les plus récents développements technologiques et thérapeutiques. Ainsi, le rôle de la radiologie a connu un essor rapide en médecine gériatrique. Compte tenu de la complexité des cas et de l’augmentation des coûts, il est essentiel que le médecin de première ligne connaisse l’utilisation appropriée de l’imagerie et des interventions radiologiques.
CONCLUSION: Il existe maintenant un certain nombre de techniques radiologiques nouvelles et innovatrices pour les patients âgés. Cette revue vise à faire connaître certaines de ces techniques aux médecins de première ligne.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Japan as the front-runner of super-aged societies: Perspectives from medicine and medical care in Japan.Geriatr Gerontol Int. 2015 Jun;15(6):673-87. doi: 10.1111/ggi.12450. Epub 2015 Feb 5. Geriatr Gerontol Int. 2015. PMID: 25656311
-
The family doctor's role in the care of the elderly.Singapore Med J. 1994 Jun;35(3):290-3. Singapore Med J. 1994. PMID: 7997907
-
Frailty: Identifying elderly patients at high risk of poor outcomes.Can Fam Physician. 2015 Mar;61(3):227-31. Can Fam Physician. 2015. PMID: 25767167 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Geriatric care management for low-income seniors: a randomized controlled trial.JAMA. 2007 Dec 12;298(22):2623-33. doi: 10.1001/jama.298.22.2623. JAMA. 2007. PMID: 18073358 Clinical Trial.
-
Addressing the needs of elderly radiology patients.Radiol Technol. 1995 May-Jun;66(5):299-304; quiz 305-6. Radiol Technol. 1995. PMID: 7644608 Review.
Cited by
-
Optimizing Primary Healthcare in Hong Kong: Strategies for the Successful Integration of Radiology Services.Cureus. 2023 Apr 2;15(4):e37022. doi: 10.7759/cureus.37022. eCollection 2023 Apr. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 37016673 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Non-Coronary, Peripheral Arterial Atherosclerotic Disease (Carotid, Renal, Lower Limb) in Elderly Patients-A Review: Part I-Epidemiology, Risk Factors, and Atherosclerosis-Related Diversities in Elderly Patients.J Clin Med. 2024 Mar 3;13(5):1471. doi: 10.3390/jcm13051471. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 38592280 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Condefer KA, Haworth J, Wilcock GK. Clinical utility of computed tomography in the assessment of dementia: a memory clinic study. Int J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2004;19(5):414–21. - PubMed
-
- Nikolaou K, Knez A, Rist C, Wintersperger BJ, Leber A, Johnson T, et al. Accuracy of 64-MDCT in the diagnosis of ischemic heart disease. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2006;187(1):111–7. - PubMed
-
- Beanlands RS, Chow BJ, Dick A, Friedrich MG, Gulenchyn KY, Kiess M, et al. CCS/CAR/CANM/CNCS/CanSCMR joint position statement on advanced noninvasive cardiac imaging using positron emission tomography, magnetic resonance imaging and multidetector computed tomographic angiography in the diagnosis and evaluation of ischemic heart disease—executive summary. Can J Cardiol. 2007;23(2):107–19. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bordeleau E, Lamonde A, Prenovault J, Belblidia A, Coté G, Lespérance J, et al. Accuracy and rate of coronary artery segment visualization with CT angiography for the non-invasive detection of coronary artery stenoses. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2007;23(6):771–80. Epub 2007 Jan 10. - PubMed
-
- Gaemperli O, Schepis T, Koepfli P, Valenta I, Soyka J, Leschka S, et al. Accuracy of 64-slice CT angiography for the detection of functionally relevant coronary stenoses as assessed with myocardial perfusion SPECT. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2007;34(8):1162–71. Epub 2007 Jan 12. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials