IL-12 enhances CTL synapse formation and induces self-reactivity
- PMID: 19155481
- PMCID: PMC2630174
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.182.3.1351
IL-12 enhances CTL synapse formation and induces self-reactivity
Abstract
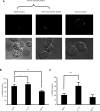
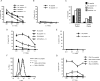
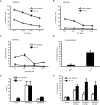
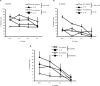
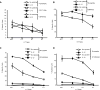
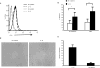
Immunological synapse formation between T cells and target cells can affect the functional outcome of TCR ligation by a given MHC-peptide complex. Although synapse formation is usually induced by TCR signaling, it is not clear whether other factors can affect the efficiency of synapse formation. Here, we tested whether cytokines could influence synapse formation between murine CTLs and target cells. We found that IL-12 enhanced synapse formation, whereas TGFbeta decreased synapse formation. The enhanced synapse formation induced by IL-12 appeared to be functional, given that IL-12-treated cells could respond to weak peptides, including self-peptides, to which the T cells were normally unresponsive. These responses correlated with expression of functionally higher avidity LFA-1 on IL-12-treated CTLs. These findings have implications for the function of IL-12 in T cell-mediated autoimmunity.
Figures
References
-
- Hemmer B, Gran B, Zhao Y, Marques A, Pascal J, Tzou A, Kondo T, Cortese I, Bielekova B, Straus SE, McFarland HF, Houghten R, Simon R, Pinilla C, Martin R. Identification of candidate T-cell epitopes and molecular mimics in chronic Lyme disease. Nat Med. 1999;5:1375–1382. - PubMed
-
- Hemmer B, Pinilla C, Appel J, Pascal J, Houghten R, Martin R. The use of soluble synthetic peptide combinatorial libraries to determine antigen recognition of T cells. J Pept Res. 1998;52:338–345. - PubMed
-
- Mason D. A very high level of crossreactivity is an essential feature of the T-cell receptor. Immunol Today. 1998;19:395–404. - PubMed
-
- Kersh GJ, Allen PM. Essential flexibility in the T-cell recognition of antigen. Nature. 1996;380:495–498. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

